Fig. 1.
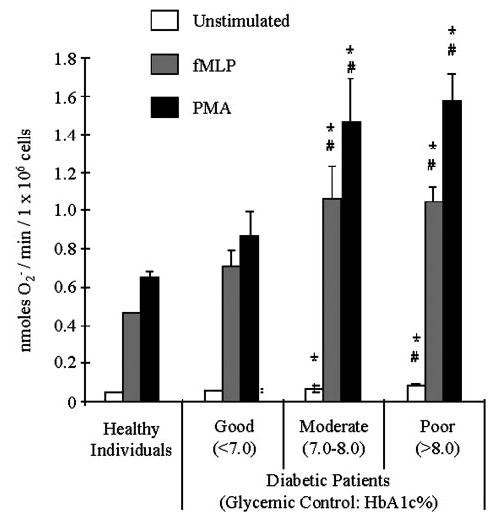
Neutrophils from diabetic subjects generate more O2− anion. Diabetic individuals were grouped into three categories based on glycemic control as defined by the American Diabetes Association. Rates of O2− release by neutrophils obtained from healthy individuals and patients with good (HbA1c 3 7.0%), moderate (HbA1c between 7.0% and 8.0%), and poor (HbA1c >8.0%) glycemic control are presented. Cells were stimulated with 1.0 μM fMLP or 300 nM PMA, and O2− release was measured as described in Materials and Methods. Neutrophils from diabetic patients with moderate and poor glycemic control exhibited greater release of O2− than neutrophils from patients with well-controlled diabetes or healthy individuals. (*, P<0.05, compared with healthy; #, P<0.05, compared with well-controlled diabetics.)
