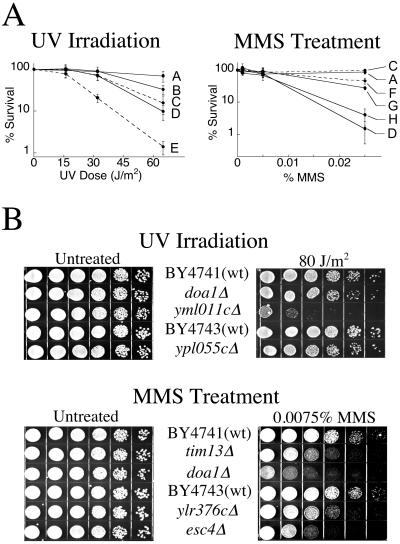
Fig 1.
Phenotypes of deletion strains as determined from individual treatment. (A) Survival curves for strains subjected to UV or MMS treatment. A, BY4743 (wild type); B, ypl055cΔ; C, BY4741 (wild type); D, doa1Δ; E, yml011cΔ; F, tim13Δ; G, ylr376cΔ; H, esc4Δ. Strains denoted by solid lines are diploid, whereas dotted lines are haploid. Error bars indicate standard deviations from a minimum of three treatments. (B) Dilution plates of deletion strains. Diploid strains are located below the parental BY4743, all other strains are haploid. Five-fold serial dilutions of ≈6 × 104 logarithmically growing cells were plated in duplicate. For UV treatment, one plate was irradiated at 80 J/m2 and incubated in the dark for 42 h at 30°C. MMS-sensitive strains were plated onto YPD–agar with or without 0.0075% MMS and incubated for 64 h at 30°C. Note that the dilution assay was conducted with doa1Δ haploid cells, whereas survival curves were constructed with the doa1Δ homozygous diploid strain, which became available during the course of this study.