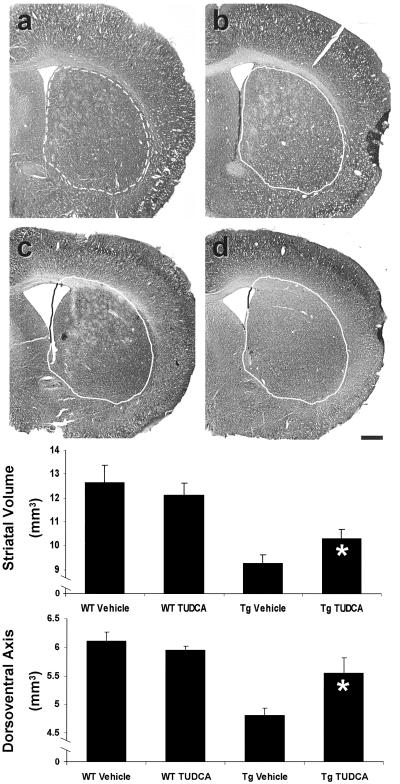
Fig 2.
TUDCA significantly reduces cerebral and striatal atrophy in R6/2 HD mice. Representative Nissl-stained striatal sections are shown for each treatment group. The untreated wt striatum (a) is outlined (broken line) for reference and superimposed (solid line) on striata from each of the other groups (b–d). Quantitation of striatal volume and dorsoventral axis measurements are represented graphically. Control R6/2 (c) striatal volume was reduced compared with wt vehicle (a) and TUDCA (b) controls. TUDCA-treated mouse striatal volume (d) was significantly larger than untreated R6/2 mice. Dorsoventral axis measurements were used to quantitate cerebral atrophy. In TUDCA-treated mice, distance of the cerebral dorsoventral axis was significantly larger than Tg controls. *, P < 0.05 for Tg TUDCA vs. vehicle. (Scale bar, 500 μm.)