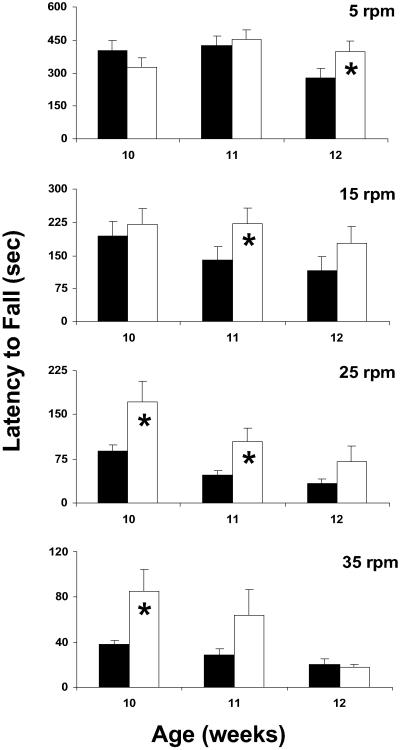
Fig 5.
TUDCA treatment improves Rota-Rod performance in an age- and speed-dependent fashion. Control and TUDCA-treated Tg mice were subjected to the Rota-Rod behavioral task as a measure of sensorimotor ability. Four different speeds with increasing task difficulty were used. Twelve-week-old TUDCA-treated R6/2 mice (white bars) exhibited significant improvement compared with control Tg mice (black bars) at slow (5 rpm) rotational velocity, whereas 11-week-old TUDCA-treated animals performed significantly better at 15 rpm. At 25 rpm, 10- and 11-week-old TUDCA-treated R6/2 mice were markedly better than control Tg animals, whereas at the highest speed (35 rpm), 10-week-old TUDCA-treated mice exhibited significant sensorimotor improvement. *, P < 0.05 for Tg TUDCA vs. vehicle.