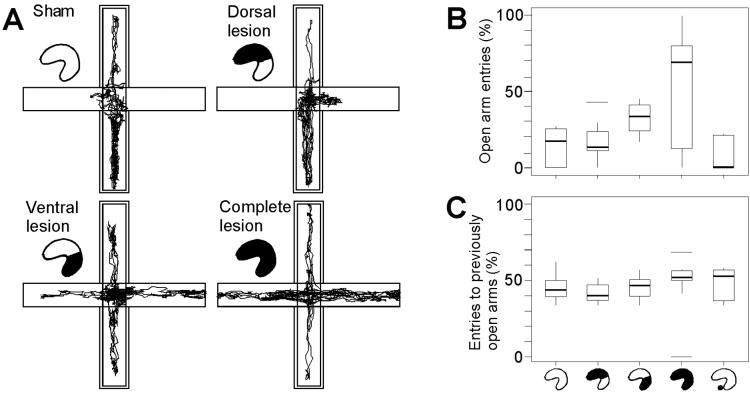
Fig 2.
Reduced open-arm avoidance after selective lesions of the ventral hippocampus. (A) Paths of representative animals with sham operations or dorsal, ventral, or complete lesions of the hippocampus, during 10 min of exposure to an elevated plus maze with two open arms. Double contours indicate enclosed arms. (B) Box plot comparing performance in rats with dorsal, ventral, or complete hippocampal lesions, or lesions of the adjacent parts of the amygdala (hippocampal icons as in Fig. 1; amygdala group to the right). The diagram shows median percentage of visits to open arms (thick horizontal line inside box), interquartile distances (boxes), upper and lower limits [Q1 − 1.5 (Q3–Q1) and Q3 + 1.5 (Q3–Q1), where Q1 and Q3 are first and third quartiles, respectively], and outliers (horizontal lines). (C) Visits to previously open arms on a subsequent trial with all arms enclosed.