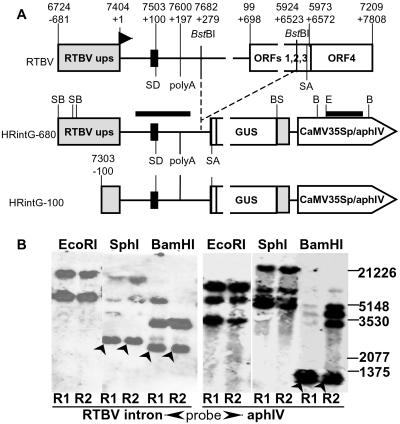
Fig 1.
Schematic map of the RTBV promoter constructs used for the generation of transgenic rice plants and Southern analyses of obtained lines. (A) The structure of the RTBV genome is shown in a linearized version on top, with the RTBV upstream promoter sequences (RTBV ups) as a gray box, the RNA leader sequence as a thin line, and the other ORFs as boxes. The positions of the splice donor (SD) and splice acceptor (SA) (77), the first short ORF in the leader (black box), and the RTBV polyadenylation signal (polyA) are marked. Sequence coordinates and positions with respect to the transcription start site (marked by a bent arrow at +1) are indicated, and the BstBI restriction sites used to generate the recombined intron (32) are shown. The GUS expression constructs mentioned in the text are shown below. GUS is fused to the RTBV ORF4, and translation of the spliced mRNA starts with the short ORF in the leader. In HRintG-680, the position of SphI (S), BamHI (B), and EcoRI (E) and the positions of probes (black bars) used for Southern analyses are shown. (B) Southern blot analysis of hemizygous R1 and R2 plants. Bands corresponding to predictable fragments are marked by arrowheads.