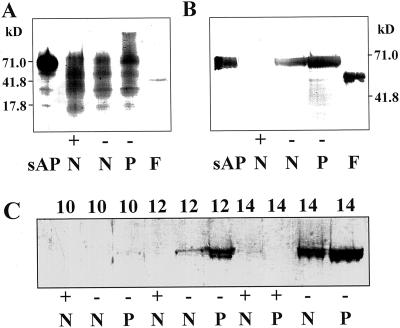
Figure 2.
Acid phosphatase secreted from P-deficient proteoid roots is a glycoprotein. A, SDS-PAGE gel blot stained with ConA-biotin to detect glycoproteins in partially purified lupin sAPase (0.08 μg of protein), purified sAPase fusion protein (F, 0.022 μg of protein), and 14- to 16-DAE cell-free extracts from +P normal roots (+, N, 0.25 μg of protein), −P normal roots (−, N, 0.15 μg of protein), and −P proteoid roots (−, P, 0.15 μg of protein). B, SDS-PAGE gel immunoblot using APase antiserum following periodate oxidation showing expression of the APase protein in 14- to 16-DAE cell-free extracts from +P normal root (+, N, 5 μg of protein), −P normal root (−, N, 5 μg of protein), and −P proteoid root (−, P, 5 μg of protein) tissues of 16-DAE white lupin. Lanes sAP (0.30 μg of protein) and F (0.040 μg of protein) contain partially purified lupin sAPase and purified APase fusion protein, respectively. C, SDS-PAGE gel immunoblot using APase antiserum following periodate oxidation showing expression of the APase protein in cell-free extracts from developing roots of lupin. Each lane contains 12.5 μg of protein from normal (N) or proteoid (P) root tissue under +P (+) or −P (−) conditions from 10 to 14 DAE. The numbers at the side of each blot indicate the molecular mass of protein markers in kD.