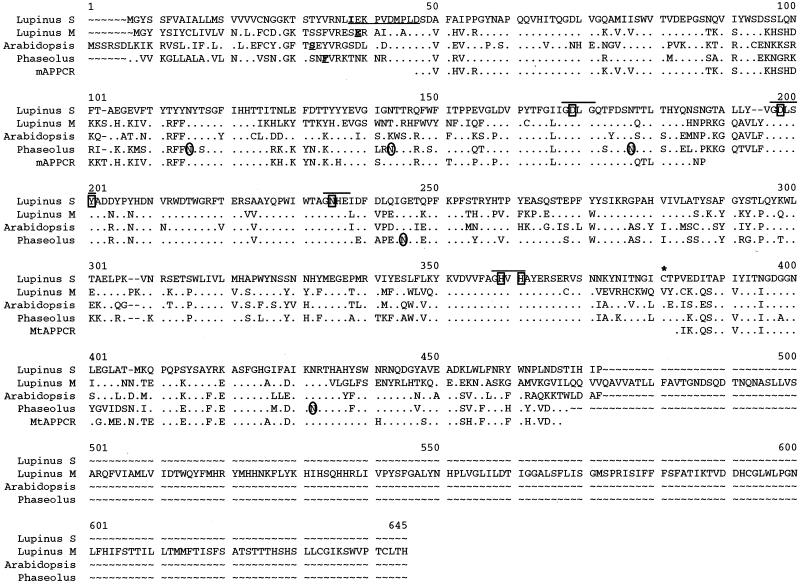
Figure 3.
Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequences of four complete APase proteins and two APase PCR products. The underlined, bold single amino acids indicate the start of the mature white lupin (Lupinus) mAPase (GenBank accession no. AB0233385), Arabidopsis purple acid phosphatase (PAP) (SwissProt accession no. Q38924), and P. vulgaris PAP (GenBank accession no. AJ001270) proteins. The 10 underlined amino acids in the white lupin sAPase sequence indicate the amino acids determined from N-terminal analysis of the purified sAPase protein. Bold lines are above blocks of amino acid residues surrounding the seven metal ligating residues (indicated by a box). The conserved Cys residue (marked by an asterisk) represents a possible site of disulfide bridge between monomers. The circled Asn (N) residues represent glycosylation sites previously determined for the P. vulgaris PAP. Identical residues are identified by dots (●). Dashed lines (∼) indicate gaps introduced in the sequences to maximize similarity. Amino acid position numbers are indicated above the sequence (Lupinus S, lupin sAPase; Lupinus M, lupin mAPase; Arabidopsis, Arabidopsis-secreted PAP; Phaseolus, red kidney bean PAP; mAPPCR, mAPase PCR product; MtAPPCR, Medicago truncatula APase PCR product).