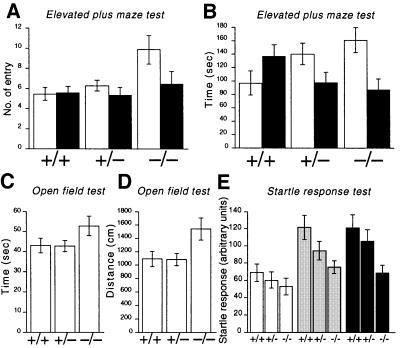
Fig. 3. Anxiety-related behaviors of wild-type (+/+), heterozygote (+/–) and homozygous mutant mice (–/–). (A and B) Elevated plus-maze test for a total of 5 min. The number of entries into each arm (A) and total time spent in each arm (B) are summarized for each genotype. Open columns: open arms; filled columns: closed arms. Entries into open arms are significantly increased in homozygous mutant mice compared with wild-type (P <0.01) and heterozygous mutant mice (P <0.05). +/+, n = 20; +/–, n = 22; –/–, n = 7. (C and D) An open-field test for a total of 2.5 min. Total locomotion time (C) and total path length (D) are summarized for each genotype. Homozygous mutant mice show significantly increased path length compared with heterozygous mutant mice (P <0.05). +/+, n = 20; +/–, n = 22; –/–, n = 9. (E) Startle responses to various intensities of sound pulses. Stimuli of 105 dB (open columns), 115 dB (gray columns) and 120 dB (filled columns) were given. Homozygous mutant mice show significantly decreased responses to sound stimuli of 115 and 120 dB compared with wild-type mice (P <0.05 for both sound stimuli). +/+, n = 11; +/–, n = 10; –/–, n = 7.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.