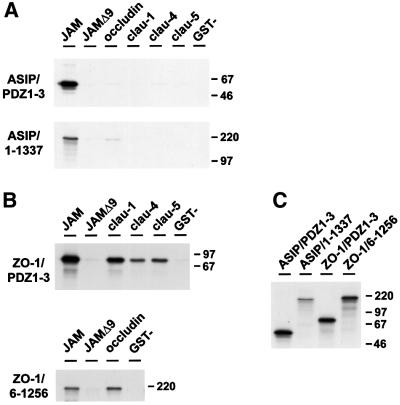
Fig. 4. ASIP interacts exclusively with JAM. (A) ASIP PDZ domains 1–3 (ASIP PDZ1–3) or full-length ASIP (ASIP 1–1337) were transcibed in vitro from the T7 promoter or the T3 promoter, respectively, and translated in the presence of [35S]methionine. Recombinant proteins were incubated with GST fusion proteins containing the cytoplasmic domains of JAM (JAM), the cytoplasmic domain of JAM truncated by nine C-terminal amino acids (JAMΔ9), the C-terminal cytoplasmic domains of occludin (occludin), claudin-1 (clau-1), claudin-4 (clau-4) and claudin-5 (clau-5), or with GST alone. (B) GST fusion proteins described in (A) were incubated with in vitro translated fragments encompassing PDZ-domains 1–3 (ZO-1/PDZ1–3) or amino acids 6–1256 (ZO-1/6–1256) of ZO-1. (C) Equal aliquots of each translation reaction were loaded separately to analyse the translation efficiency. Note that full-length ASIP is generated less efficiently, most likely due to the use of T3 promoter rather than the T7 promoter used for ASIP PDZ1–3. In contrast to ZO-1 fragments, which interacted specifically with all GST fusion proteins, ASIP interacted strongly only with GST–JAM.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.