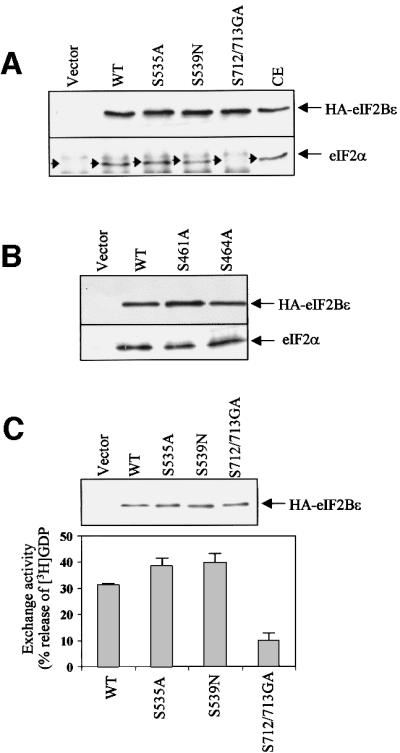
Fig. 9. Effects of point mutations on the interaction of eIF2Bε with eIF2 in vivo and on eIF2Bε activity. (A and B) HEK293 cells were transfected with vectors encoding wild-type eIF2Bε, the indicated point mutants, or vector alone, as a negative control. eIF2Bε was then immunoprecipitated from cell lysates using anti-HA antibodies and analysed by SDS–PAGE followed by immunoblotting with antibodies to either eIF2α or HA (as a loading control). (C) eIF2Bε was immunoprecipitated from transfected HEK293 cells using anti-HA antibodies and then used in eIF2B activity assays, as described in Materials and methods. Immunoprecipitations were carried out in triplicate, two for the exchange assay and one for SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting using anti-HA antibodies to check for equal levels of eIF2Bε (upper panel). The results show the average of two independent experiments ± SD and are expressed as the percentage of [3H]GDP released from complexes with eIF2, corrected for the low activity seen with samples from cells transfected with the empty vector (lower panel). Similar data were obtained in four sets of experiments.
