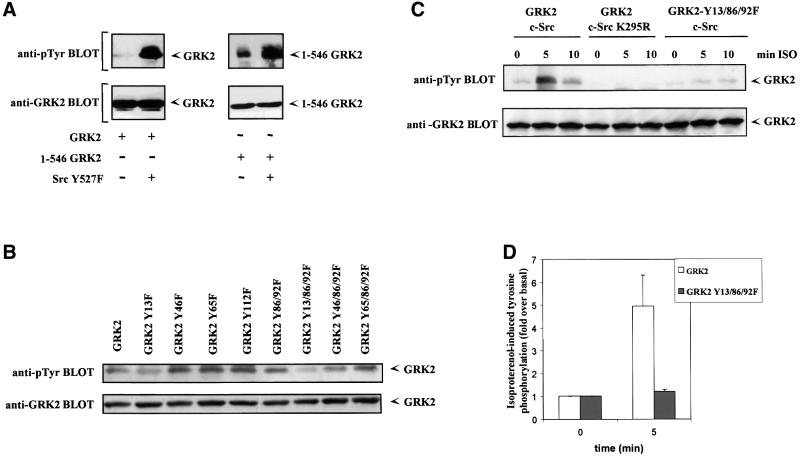
Fig. 7. Identification of critical tyrosine residues involved in GRK2 phosphorylation by c-Src. (A) Cos-7 cells were transiently transfected with wild-type GRK2 or the GRK2 deletion mutant 1–546, and the constitutively active c-Src Y257F or empty vector as indicated. Immunoprecipitates of GRK2 were analyzed with an anti-phosphotyrosine monoclonal antibody as detailed in Materials and methods (top panels). After stripping, the presence of GRK2 was analyzed in the same gel as in the lower panel of Figure 6A. Gels representative of two independent experiments are shown. (B) Similar experiments were performed in Cos-7 cells transiently transfected with the constitutively active c-Src Y527F mutant and wild-type GRK2 or the indicated tyrosine to phenylalanine mutants of GRK2. Tyrosine phosphorylation of GRK2 (upper panel) was measured by scanner laser densitometry, and the data normalized to the amount of GRK2 protein present in the immunoprecipitates as assessed with a GRK2 antibody (lower panel). A gel representative of two independent experiments is shown. (C) HEK-293 cells transiently transfected with β2AR and the indicated combinations of GRK2, GRK2-Y13/86/92F, wild-type c-Src or an inactive c-Src K295R mutant were stimulated or not (0 min) for the indicated times with 1 µM isoproterenol (ISO) as described in Materials and methods. Tyrosine phosphorylation of GRK2 was determined as in previous panels. Tyrosine phosphorylation levels of GRK2 and the GRK2 Y13/86/92F mutant in the presence of β2AR and wild-type c-Src after 5 min of agonist stimulation were compared in more detail by laser densitometry (D). Non-stimulated controls were taken as the basal condition. Data are the mean ± SE of three independent experiments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.