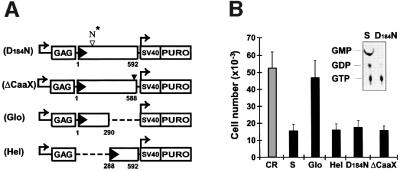
Fig. 6. The helical domain of GBP-1 is sufficient to inhibit endothelial cell proliferation. (A) Schematic presentation of the retroviral expression vector pBabePuro encoding various mutants of GBP-1: GTPase-deficient (D184N-GBP-1, D184N) and isoprenylation motif-deleted (ΔCaaX-GBP-1, ΔCaaX) GBP-1, separated N-terminal globular domain (Glo-GBP-1, Glo) and C-terminal helical domain (Hel-GBP-1, Hel). The numbers refer to the positions of the amino acids in GBP-1. The D to N mutation in the GTPase motif is indicated by an open triangle and the black triangle indicates the TAA stop codon inserted upstream of the encoded CaaX motif. (B) Proliferation experiments with transduced HUVEC in the presence of AGF (10 ng/ml) and GTPase assay of purified wild-type GBP-1 and D184N-GBP-1 (insert).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.