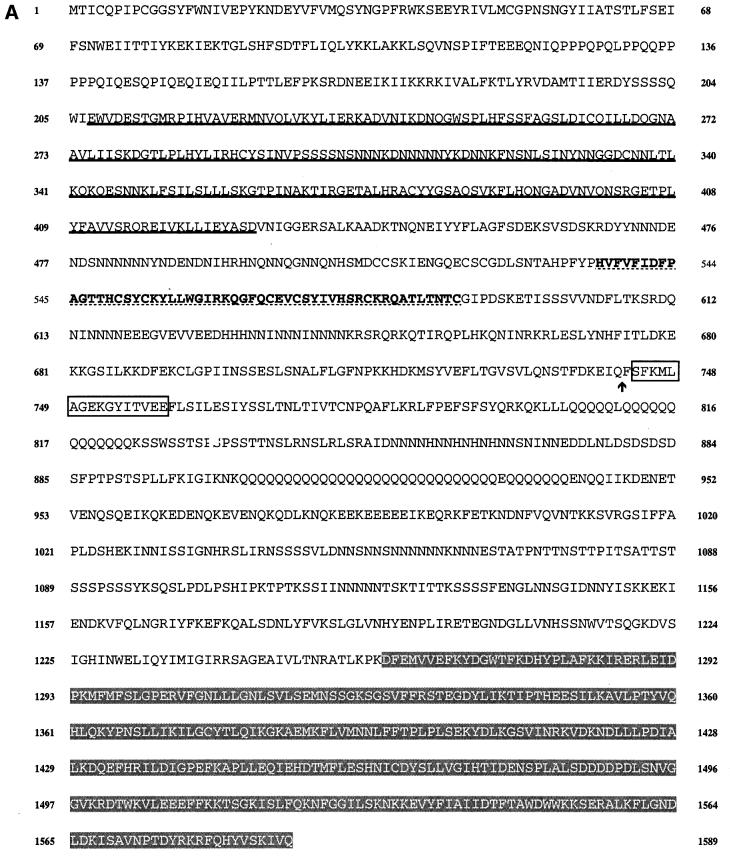
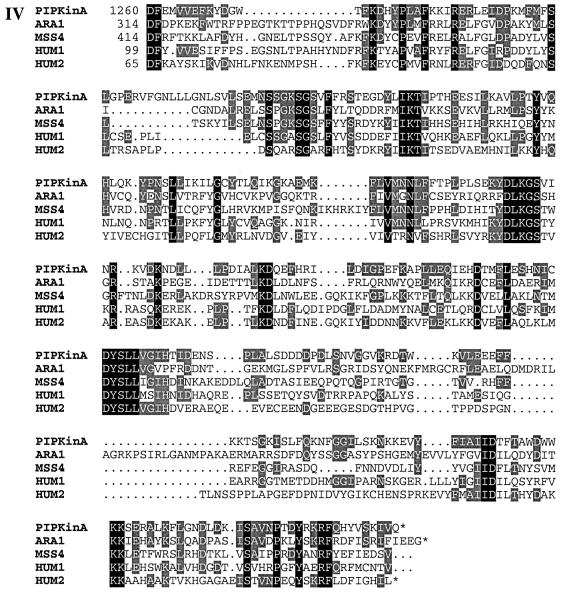
Fig. 1. (A) Sequence of the PIPkinA protein. The protein sequence of the PIPkinA open reading frame is shown. The areas of homology (as determined by BLAST sequence similarity searching) are indicated with the ankyrin-repeat domain underlined, the DAG-binding domain in bold with dotted underlining, the α-actinin homology domain boxed and the PIP kinase domain shaded. The position of the single small intron is marked with an arrow. The nucleotide sequence has been submitted to the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank database under accession No. AF339903. (B) Sequence comparisons between PIPkinA and other proteins. Searching the EMBL database with the PIPkinA protein sequence revealed several areas of homology to other proteins which are shown here. (I) The homology between the DAG-binding domain of PIPkinA and the first copies of the repeat sequence from Drosophila PKC (Rosenthal et al., 1987) and bovine PKCγ (Coussens et al., 1986). The conserved His and Cys residues defining the motif are shaded and residues conserved in PIPkinA are underlined. N- and C-terminal deletion of the motif in PKCγ has revealed the N-terminal histidine residue to be essential, whereas the C-terminal cysteine can be deleted without loss of binding (Quest et al., 1994b). The spacing between these two residues and the central motif is different in PIPkinA with the insertion of extra amino acids, showing that the spacing is not critical for DAG association. (II) The sequence of the five ankyrin repeats found in PIPkinA with a consensus sequence (as defined by Bork, 1993) shown for comparison. Residues matching the consensus are underlined in each copy of the repeat. These 33 amino acid repeats have been found in a wide range of proteins including transcription factors such as SWI6 (Breeden and Nasmyth, 1987) and signalling proteins such as the Drosophila notch protein (Kidd et al., 1986). (III) The short stretch of sequence homology between PIPkinA and human α-actinin from skeletal muscle (SM) and non-muscle (NM) (Beggs et al., 1992). Residues conserved in PIPkinA are underlined. (IV) Alignment of the C-terminal region of PIPkinA with the PIPKs from Arabidopsis (ARA1) (Mikami et al., 1998), S.cerevisiae (MSS4) (Yoshida et al., 1994), human type 1α (HUM1) and human type IIα (HUM2) (Boronenkov and Anderson, 1995). Amino acids conserved in all five sequences are shaded in black and those conserved with PIPkinA are shaded in grey.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.