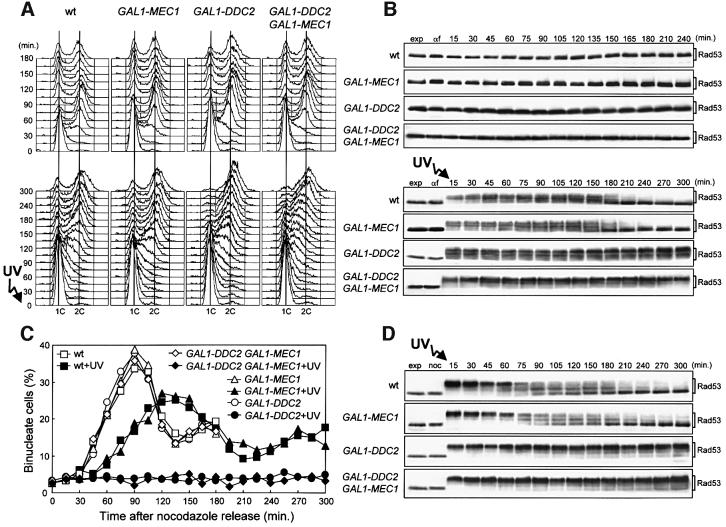
Fig. 6. DDC2 overexpression leads to prolonged G2/M cell cycle arrest after checkpoint activation. Strains were as follows: wild type [URA3 YCplac33] (YLL827), wild type [URA3 GAL1–MEC1] (YLL826), GAL1–DDC2 [URA3 YCplac33] (YLL837) and GAL1–DDC2 [URA3 GAL1–MEC1] (YLL836). (A and B) Cell cultures growing logarithmically in YEP-raf were synchronized with α-factor. Galactose was added 2.5 h before α-factor addition. α-factor-synchronized cells were released from the block at time zero [(B), αf] in YEP-raf-gal or were UV irradiated (40 J/m2) prior to release in YEP-raf-gal. Samples of untreated (top) and UV-treated (bottom) cell cultures were collected at the times indicated after α-factor release to analyze the DNA content by FACS (A) and protein extracts by western blotting, using anti-Rad53 antibodies (B). (C and D) Cell cultures growing logarithmically in YEP-raf were synchronized with nocodazole. Galactose was added 2 h before nocodazole addition. Nocodazole-synchronized cells were released from the block at time zero [(D), noc] in YEP-raf-gal or were UV irradiated (50 J/m2) prior to release in YEP-raf-gal. Samples of untreated and UV-treated cell cultures were collected at the times indicated after nocodazole release to score for the percentage of binucleate cells by propidium iodide staining (C) and to analyze protein extracts from the UV-treated cell cultures by western blotting, using anti-Rad53 antibodies (D). exp, exponentially growing cells. In all the experiments, samples were withdrawn from the UV-treated cultures at times zero and 120 min, and appropriate dilutions were plated on YEPD plates to score for colony-forming units (see text for the percentage of cell survival).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.