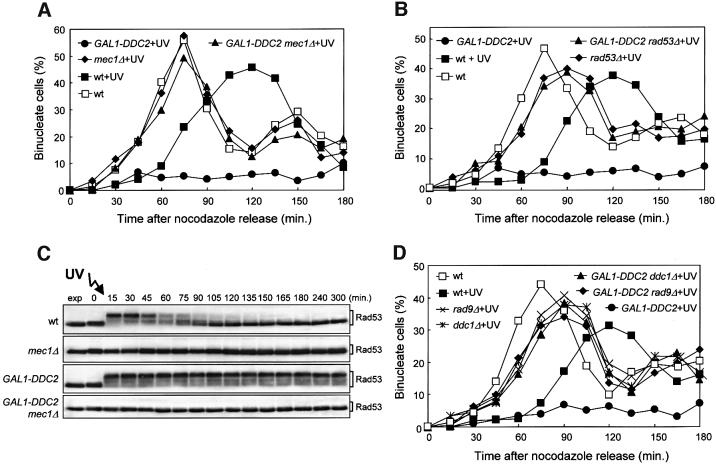
Fig. 7. Requirement of checkpoint genes for the Ddc2-dependent DNA damage-induced cell cycle arrest. Strains were as follows: wild type (K699), GAL1–DDC2 (YLL279.2), mec1Δ sml1Δ (YLL490), GAL1–DDC2 mec1Δ sml1Δ (DMP3462/2B), rad53Δ sml1Δ (YLL509), GAL1–DDC2 rad53Δ sml1Δ (DMP3356/4A), rad9Δ (YLL157), GAL1–DDC2 rad9Δ (DMP3392/4A), ddc1Δ (YLL244) and GAL1–DDC2 ddc1Δ (DMP3463/10C). Cell cultures growing logarithmically in YEP-raf were synchronized with nocodazole. Galactose was added 2 h before nocodazole addition and nocodazole-synchronized cells were released from the block at time zero in YEP-raf-gal or were UV irradiated (50 J/m2) prior to release in YEP-raf-gal. (A, B and D) Untreated and UV-treated cell cultures were scored at the times indicated for the percentage of binucleate cells by propidium iodide staining. (C) Protein extracts from the UV-treated cell cultures were analyzed by western blotting, using anti-Rad53 antibodies. exp, exponentially growing cells.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.