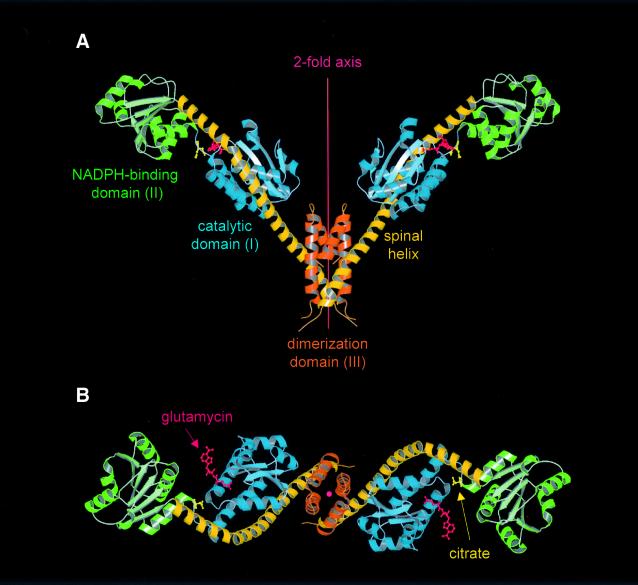
Fig. 2. Structure of the GluTR dimer viewed (A) perpendicular to and (B) along the 2-fold axis. Monomers consist of three structural domains: (I) an N-terminal catalytic domain (blue); (II) an NAPDH-binding domain (green); and (III) a C-terminal dimerization domain (orange)—connected by an extended 18-turn ‘spinal’ α-helix (dark-yellow). Glutamycin (red) binds at the catalytic domain. At the deep end of the large crevice between domains I and II a citrate anion (yellow) is bound. Figures 2, 3 and 5 were generated using MOLSCRIPT (Kraulis, 1991) rendered with RASTER3D (Merrit and Murphy, 1994).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.