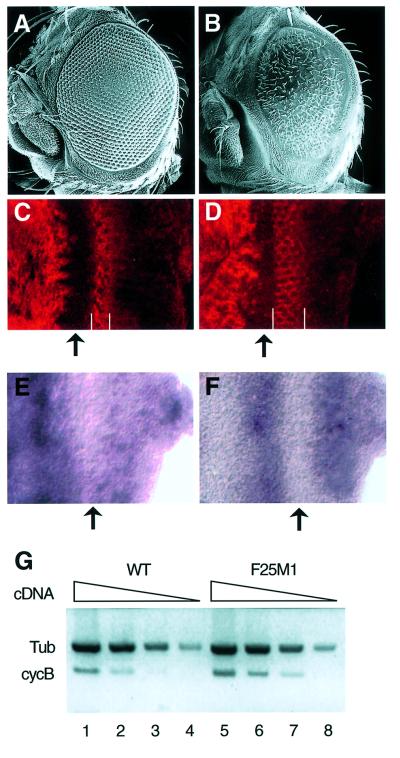
Fig. 2. Rough eye phenotype and ectopic expression of cyclin B in the transgenic flies expressing C-truncated dMyb. (A and B) Scanning electron micrographs of adult eyes. Normal compound eye of wild type (A) and severe rough eye of GMR–dMybΔC-F25 (B) flies. (C and D) Immuno-staining of the eye imaginal disc with anti-cyclin B antibody. High magnification of the eye disc is indicated. Eye discs were prepared from wild-type (C) and GMR–dMybΔC-F25 (D) flies. The widths of the cyclin B-expressing cells are indicated by white bars. Anterior is to the left, dorsal is up. (E and F) Expression of cycB mRNA in the eye imaginal disc. In situ hybridization was performed using a cycB-specific anti-sense RNA probe. High magnification of the eye disc is indicated. The cycB mRNA was detected at the whole region anterior to the MF and in the whole region posterior to the MF in the wild-type eye imaginal disc (E), whereas a strong cycB mRNA signal was detected in the broad stripe posterior to the MF in the GMR–dMybΔC-F25 disc (F). Anterior is to the left, dorsal is up. (G) RT–PCR analysis of the cyclin B mRNA. Poly(A)+ RNAs were prepared from the wild-type and GMR–dMybΔC-F25 eye discs and the cDNAs corresponding to the cyclin B and β1-tubulin genes were sythesized. Using various amounts of the first-strand synthesis reaction mixture (5, 0.5, 0.1 and 0.02 µl for lanes 1–4 and 5–8, respectively), the DNA fragments were then amplified. Quantification of the PCR products were performed by Southern blot analysis.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.