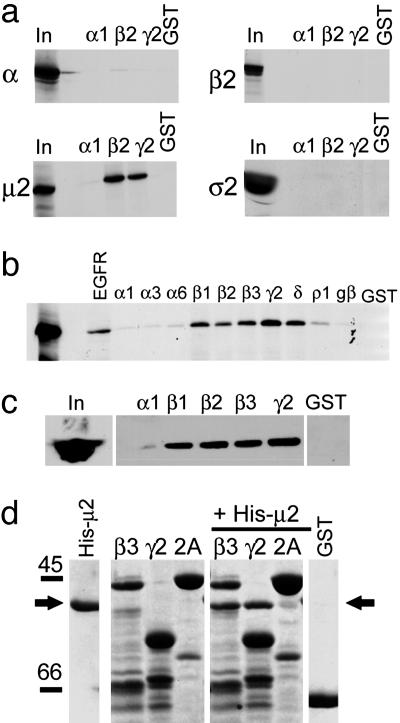
Fig. 1.
Identification of a direct interaction between GABAAR ICDs and the μ2 subunit of the AP2 adaptor complex. (a) GABAAR ICDs interact with the μ2 subunit of AP2. 35S-labeled α, β2-, μ2-, and σ2 adaptins were synthesized by coupled transcription translation in vitro and incubated with GST-α1, GST-β2 and GST-γ2 GABAAR ICDs, or GST alone. Bound material was separated by SDS/PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. Input (In) represents 10% of total amount of radiolabeled protein added to assay. (b) Further analysis of GABAAR subunit specificity of μ2 binding. μ2 adaptin was synthesized as above and exposed to various GABAAR ICDs, and bound material was separated by SDS/PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. In represents 10% of total amount of radiolabeled protein added to assay. EGFR and GST are positive and negative controls for μ2 binding, respectively. (c) GABAAR ICDs bind μ2 from brain extract. GABAAR ICDs immobilized on glutathione agarose beads were incubated with solubilized brain extracts. Bound material was resolved by SDS/PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies to μ2. In represents 25% of the material used for each experiment. (d) Direct binding of purified bacterially expressed His-tagged μ2 (residues 156-435) to GABAAR GST-β3 and GST-γ2 ICD but not to either GST-Synaptotagmin 1 C2A (2A) domain or GST alone. GST fusion proteins were exposed to His-μ2, and complexes were resolved by SDS/PAGE, followed by staining the gel with Coomassie brilliant blue. His-μ2 represents purified His-μ2 alone. β3, γ2, and 2A represent GST-β3, GST-γ2, or GST-synaptotagmin 2A (2A) domain resolved on the gel either alone to show fusion protein bands or after exposure to His-μ2. The arrow denotes bound His-μ2 detected by Coomassie staining.