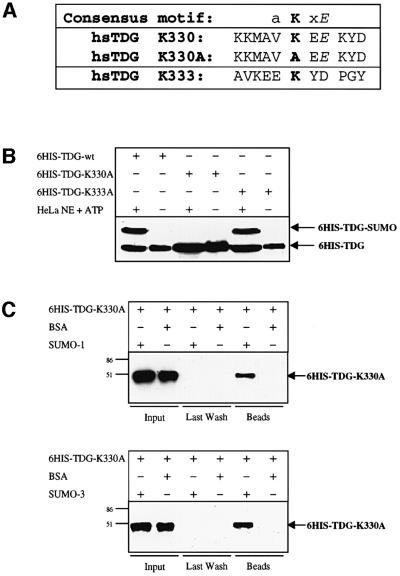
Fig. 4. Mapping of the sumoylation acceptor site within human TDG. (A) A four amino acid consensus sumoylation motif has been proposed (a = aliphatic amino acid). The amino acid sequence surrounding the candidate acceptor lysine K330 of human TDG is shown. K330A is the sequence resulting from mutagenesis of K330 to alanine; K333 is a conserved residue adjacent to K330 that was mutated to alanine as a control. (B) A 100 ng aliquot of purified His6-tagged wild-type or mutant (K330A, K333A) TDG proteins was subjected to modification by incubation with 25 µg of HeLa nuclear extract (NE) in the presence of 10 mM ATP. Western blotting revealed efficient sumoylation of the wild-type and the K333A TDG variants but no detectable modification of the K330 mutant. (C) The modification-deficient K330A mutant can still interact with SUMO-1 and SUMO-3. His6-tagged K330A mutant protein (600 ng) was incubated together with 20 µl of SUMO-1, SUMO-3 or BSA-coated affinity beads for co-precipitation. Subsequent immunoblotting of input, last wash and bead fractions revealed a specific retention of the mutant TDG protein (arrows) on the SUMO-1 and SUMO-3 but not on the BSA beads. The input represents 16% of the total amount of mutant TDG protein used. All western blots shown were performed with the polyclonal anti-TDG antibody.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.