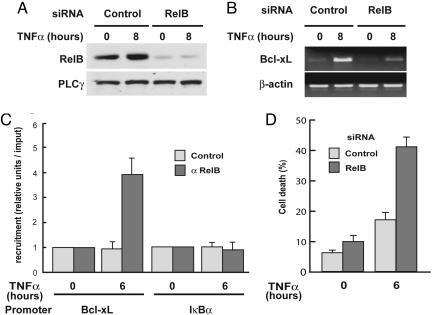
Fig. 5.
RelB knockdown by RNAi blocks Bcl-xL expression and promotes TNF-α-induced apoptosis in RelA-deficient MEFs. (A) RelB protein levels are efficiently knocked down by RNAi. RelA-deficient MEFs were transfected with either a siRNA oligonucleotide targeting RelB or a scrambled control. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were treated with TNF-α for 8 h or left untreated and then harvested and analyzed for RelB protein expression by immunoblotting. (B) RelB knockdown by RNAi prevents TNF-α induction of Bcl-xL expression in RelA-deficient MEFs. RelA-deficient MEFs were transfected with either a siRNA oligonucleotide targeting RelB or a scrambled control. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were treated with TNF-α for 8 h or left untreated and then harvested and analyzed for Bcl-xL and β-actin expression by using semiquantitative RT-PCR. (C) RelB is bound to the Bcl-xL promoter after TNF-α stimulation in RelA-deficient MEFs. RelA-deficient MEFs were treated with TNF-α for 6 h or left untreated, and recruitment of RelB to the Bcl-xL and IκBα promoters was examined by ChIP experiments followed by quantitative PCR analysis. The results are means ± SE of three independent experiments normalized to inputs that reflect relative amounts of sonicated DNA fragments present before immunoprecipitation. (D) RelB knockdown by RNAi promotes TNF-α-induced apoptosis in RelA-deficient MEFs. RelA-deficient MEFs were transfected with either a siRNA oligonucleotide targeting RelB or a scrambled control. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were treated with TNF-α (20 ng/ml)for 6 h or left untreated, collected, and incubated with annexin V-FITC for 20 min and analyzed by flow cytometry. Shown are means ± SE of three independent experiments.