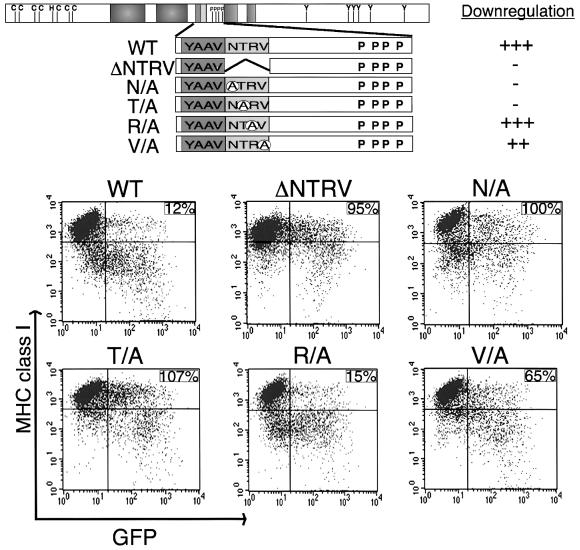
Fig. 4. NTRV sequence at the cytoplasmic region of K3 is required for MHC class I down-regulation. A schematic of the location of various mutations of the K3 protein is shown at the top. Five mutations, K3 ΔNTRV (ΔNTRV), K3 N156/A (N/A), K3 T157/A (T/A), K3 R158/A (R/A) and GFP K3 V159/A (V/A), were introduced into K3. Each mutant is described in greater detail in the text. Along the right side, the ability of wild-type K3 and each mutant to down-regulate MHC class I, as shown below the schematic, was given a relative score. ‘+++, ++, + and –’ indicate strong, weak, very weak and no activity of the K3 mutant in MHC class I down-regulation, respectively. The differential MHC class I down-regulation activity of several K3 mutants is shown below the schematic. To examine activity of K3 and its mutants in MHC class I down-regulation, BJAB cells were electroporated with pTracer–GFP–K3 (WT) or one of the K3 mutant vectors. Cell surface level of MHC class I was assessed 48 h post-transfection by staining for MHC class I (y axis) and gating the GFP-positive cell population (x axis) by flow cytometry. Numbers in the upper right side quadrant represent the MCF of MHC class I staining in the GFP-positive population, calculated as described in the legend to Figure 2. The data were reproduced in at least two independent experiments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.