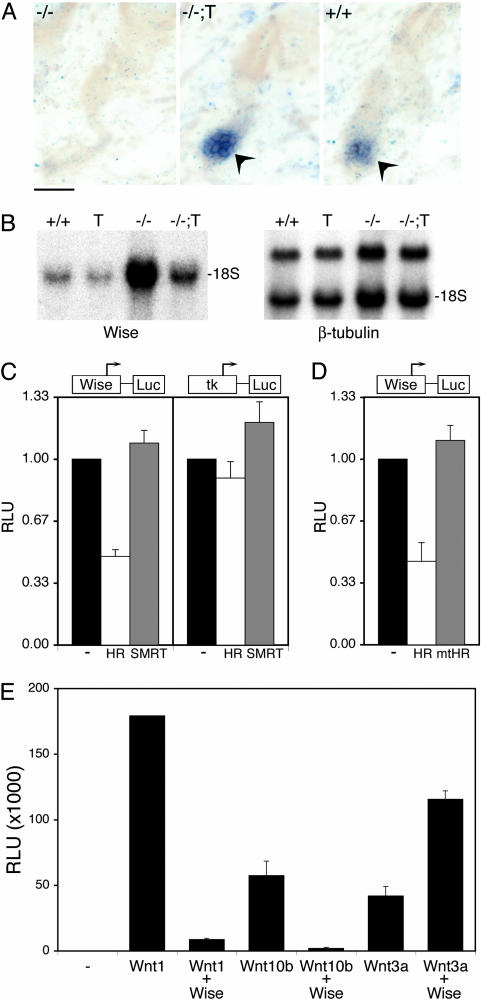
Fig. 4.
HR regulates expression of a modulator of Wnt signaling (Wise). (A) In situ hybridization for Axin2, a Wnt-responsive gene, in back skin sections from P22 mice of the indicated genotypes: -/- (Hr-/-), -/-;T (transgenic rescue), and +/+ (wild type). Arrowheads indicate Axin2 expression. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (B) Northern analysis for Wise mRNA expression using RNA from back skin of P24 mice of the indicated genotypes: +/+ (wild type); T (K14-rHr); -/-, (Hr-/-); and -/-;T (transgenic rescue). (Right) β-tubulin hybridization of an identical blot; Wise expression was normalized to β-tubulin expression. 18S, position of 18S RNA. (C) Reporter genes for the Wise promoter (Wise-Luc) and control (tk-Luc) were transfected into cells with the indicated expression vectors. (-), empty expression vector. Results were normalized to vector control for each promoter. (D) The Wise reporter gene was transfected with expression vectors for HR or a HR derivative (mtHR) that has mutated receptor-interaction domains. Equal expression of HR and mtHR was verified by Western analysis (data not shown). (E) Cells stably expressing a Wnt-responsive reporter gene (Super TOP-Flash) were transfected with the indicated expression vectors. For B–D, relative light units (RLU) is luciferase activity relative to β-gal activity (internal control). Results are the average of at least three experiments done in duplicate.