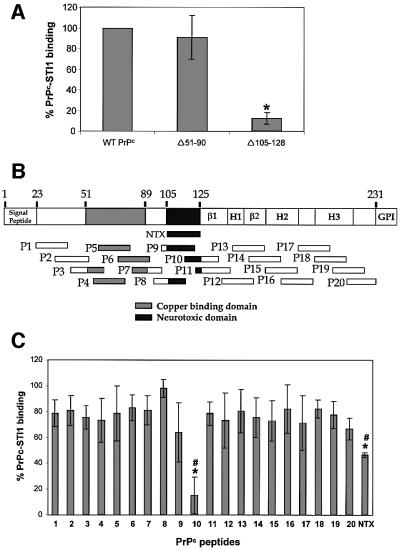
Fig. 4. Mapping the STI1 binding site in PrPc using deletion mutants and synthetic PrPc peptides. (A) Wild-type PrPc and deletion mutants Δ51–90 and Δ105–128 were incubated with [125I]His6-STI1. The binding between wild-type His6-PrPc and [125I]His6-STI1 was set to 100% (control). The results for each PrPc mutant were expressed as percentage binding compared with wild-type. *P <0.01 versus control, single mean Student’s t-test. (B) Twenty mouse PrPc peptides covering the PrPc (23–231) protein sequence were synthesized chemically as a 20mer with 10 overlapping residues. The scheme shows localization of the 20 peptides, the neurotoxic peptide (NTX) and the main PrPc domains: β1 and β2, β-sheet domains; H1, H2 and H3, α-helix domains; GPI, GPI anchor. (C) The synthetic peptides were pre-incubated with [125I]His6-STI1 followed by incubation with adsorbed His6-PrPc. Total binding between His6-PrPc and [125I]His6-STI1 was set to 100%. The results are expressed as the relative percentage of the binding produced by competition with each peptide. *P < 0.01 versus control, single mean Student’s t-test; #P < 0.01 NTX versus P10, Mann– Whitney test.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.