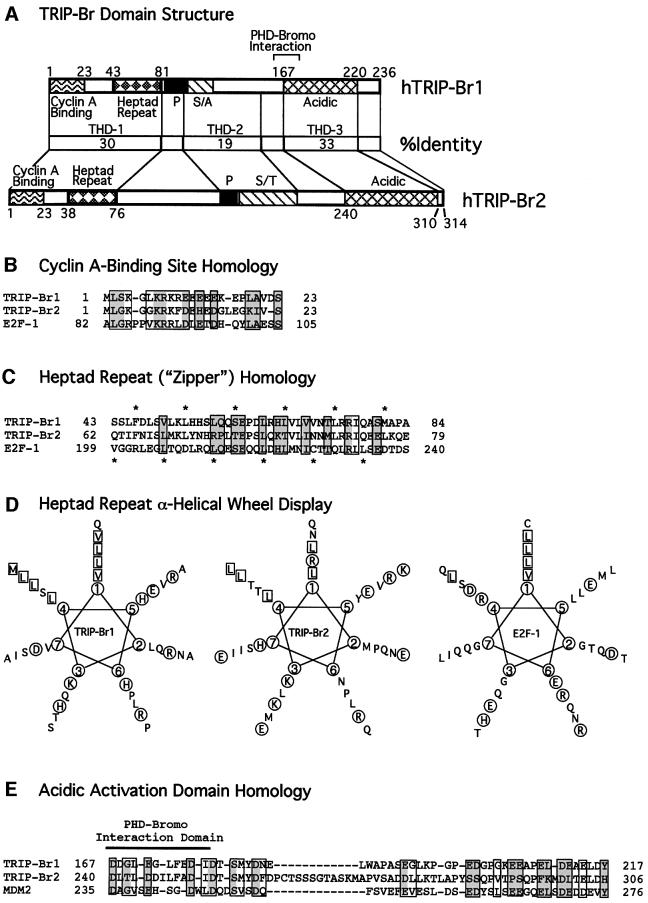
Fig. 3. Human TRIP-Br domains with homology to E2F-1 and MDM2. (A) Comparison of the domain structure and amino acid identity of the TRIP-Br proteins. The minimal region of TRIP-Br1 (aa 161–178) required for interaction with the PHD-bromodomain is indicated by brackets. P, proline-rich; S/A, serine/alanine-rich; S/T, serine/threonine-rich. (B) N-terminal sequences of the human TRIP-Br proteins are shown aligned with the cyclin A-binding domain of E2F-1. Boxed residues indicate amino acids that are similar between E2F-1 and at least one of the TRIP-Br proteins, and shaded boxes indicate residues that are identical between E2F-1 and at least one of the TRIP-Br proteins. (C) N-terminal sequences of the human TRIP-Br proteins are shown aligned with the heptad repeat region of E2F-1. Amino acids are boxed and shaded as in (B). Asterisks shown below indicate the heptad periodicity characteristic of E2F-1 and DP-1, which is also shared by the TRIP-Br proteins. Asterisks shown above indicate a novel heptad periodicity, which occurs only in the TRIP-Br proteins. (D) Amino acids in the putative heptad repeat regions of the human TRIP-Br proteins and E2F-1 are displayed in an α-helical wheel. Hydrophobic residues that occur in positions 1 and 4, corresponding to the two heptad periodicities shown in (C), are boxed. Charged residues are circled. (E) C-terminal sequences of the human TRIP-Br proteins are shown aligned with the MDM2 transactivation domain. Amino acids are boxed and shaded as in (B).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.