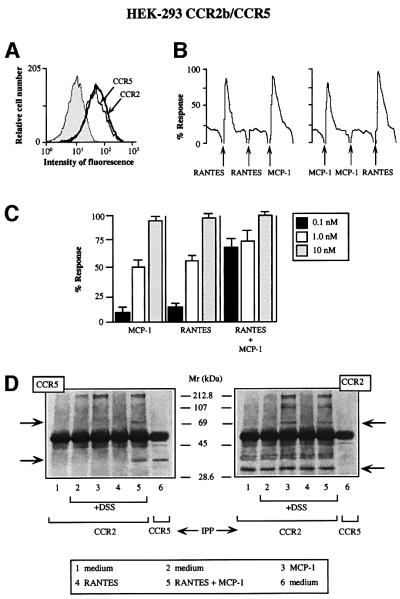
Fig. 1. Simultaneous MCP-1 and RANTES co-activation of CCR2- and CCR5-expressing cells increases sensitivity of chemokine responses and promotes their heterodimerization. (A) CCR2b/CCR5 double-transfected HEK-293 cells were incubated with biotin-labeled mAbs against CCR2 and CCR5 or their respective isotype-matched control mAbs, followed by isothiocyanate-labeled streptavidin. (B) Ca2+ mobilization was induced by treatment with 10 nM MCP-1 or 10 nM RANTES in Fluo-3-loaded CCR2/CCR5-co-transfected HEK-293 cells. Results are expressed as a percentage of the chemokine-induced calcium response. Five experiments were performed; the figure depicts one representative experiment. Arrows indicate addition of stimulus. (C) Ca2+ mobilization was determined as in (B), following stimulation with different concentrations of MCP-1 or RANTES as indicated, added separately or simultaneously. Results are expressed as a percentage of the maximum chemokine-induced calcium response. The mean ± SD of four independent experiments is shown. (D) CCR2/CCR5-co-transfected HEK-293 cells were stimulated with chemokines (10 nM for 5 min at 37°C) and, where indicated, cross-linked with 1 mM DSS. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-CCR2 antibody, electrophoresed and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The western blot was analyzed with anti-CCR5 antibody (left); as a positive control, unstimulated CCR2/CCR5-co-transfected HEK-293 cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-CCR5 antibody (lane 6). The membrane was stripped and reprobed with anti-CCR2 antibody as a control for protein loading (right). Arrows indicate the position to which monomers and dimers migrated.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.