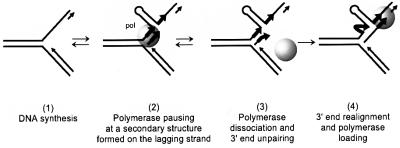
Fig. 7. Schematic representation of the slippage process at a replication fork. During DNA synthesis of a repeated sequence (step 1), the polymerase reaches a barrier on the lagging strand (a hairpin structure in our experimental system) and pauses (step 2). Polymerase dissociation occurs (step 3). If the polymerase is not able to disrupt the barrier (with its strand displacement activity), then the tip of the newly synthesized strand can unpair from its template and anneal to the second repeat beyond the barrier, allowing polymerase re-loading and resumption of the synthesis (step 4).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.