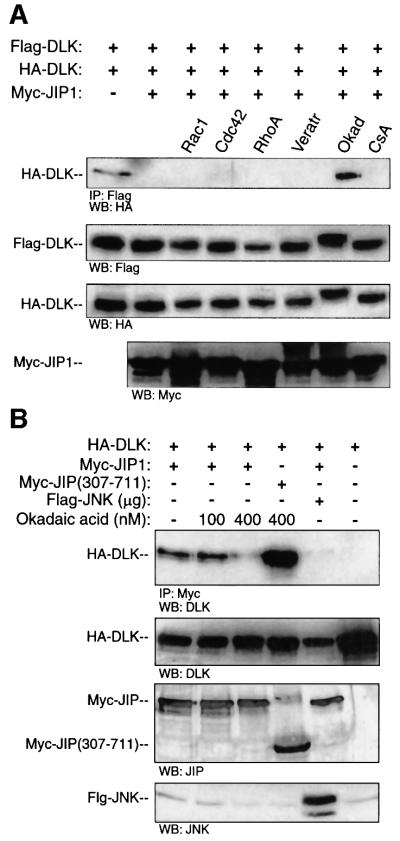
Fig. 9. Okadaic acid treatment results in decreased affinity of JIP for DLK and DLK dimerization in the presence of JIP. (A) COS 7 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding HA-DLK (0.1 µg), Flag-DLK (0.1 µg) and Myc-JIP1 (1.0 µg) as indicated. The indicated cells were transfected simultaneously with activated forms of either Myc-V12Cdc42Hs, Myc-V12Rac1 or Myc-L63RhoA. Where indicated, cells were treated for 3 h with either veratridine (20 µg), okadaic acid (400 nM) or cyclosporin A (30 µM). Flag-DLK was immuno precipitated from cell lysates; immunoprecipitated complexes were separated by SDS–PAGE and were immunoblotted with anti-HA antibody. Immunoblots from the corresponding cell lysates were used to evaluate the relative expression of Flag-DLK, HA-DLK and Myc-JIP. (B) COS 7 cells were co-transfected with plasmids encoding HA-DLK (0.5 µg) and Myc-JIP1 (0.5 µg). Cells were treated for 3 h with the indicated concentrations of okadaic acid. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody, separated by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-DLK antibody. Cell lysates from the corresponding experiments were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies to evaluate the expression of JIP and DLK. These experiments were repeated three times with similar results.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.