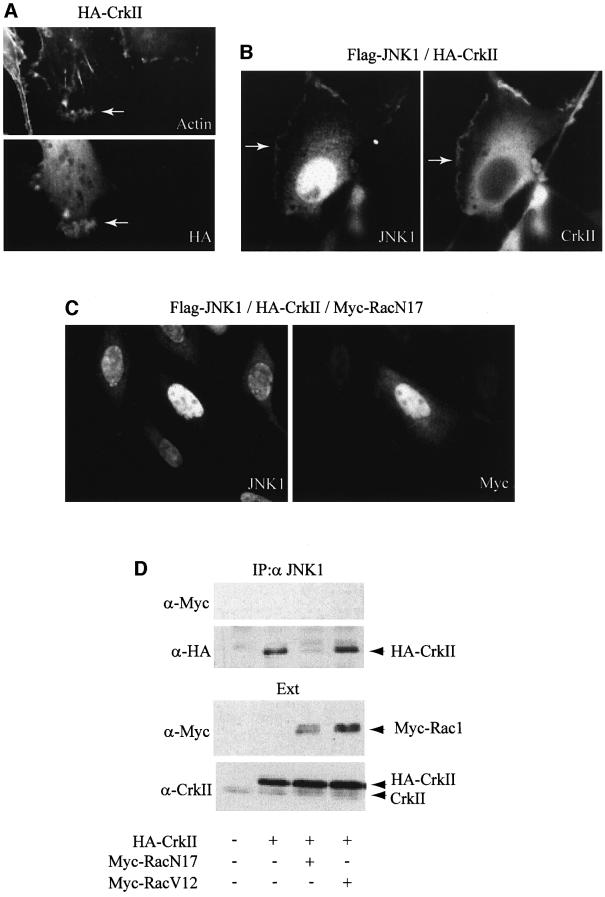
Fig. 2. CrkII interaction with JNK1, and CrkII-dependent JNK1 localization to ruffles are regulated by Rac1 activity. (A) Overexpression of CrkII induces membrane ruffling. HeLa cells were visualized by indirect immunofluorescence after transfection with HA-CrkII expression vector. Cells were stained using a mouse monoclonal anti-HA. Rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin was used to visualize filamentous actin. Membrane ruffling induced by CrkII is indicated by an arrow. (B) JNK1 localization to ruffles. HeLa cells were visualized by indirect immunofluorescence after cotransfection with Flag-JNK1 and HA-CrkII expression vectors. Cells were stained using a mouse monoclonal anti-CrkII or a polyclonal rabbit anti-JNK1 antibody as indicated. JNK1 localization to ruffles is indicated by an arrow. (C) Effect of Rac1 on JNK1 localization to ruffles. HeLa cells were visualized by indirect immunofluorescence after cotransfection with Flag-JNK1, HA-Crk and Myc-RacN17 expression vectors. Cells were stained using a rabbit polyclonal anti-JNK1 antibody (left panel) or a mouse monoclonal anti-Myc antibody (right panel). Membrane ruffles were absent in all the cells transfected with Myc-RacN17 expression vector. (D) Effect of Rac1 on the CrkII–JNK1 interaction. HeLa cells were transfected with HA-CrkII plus either Myc-RacN17 or Myc-RacV12 expression vectors as indicated. Interaction between JNK1 and transfected HA-CrkII was determined by HA immunoblot on JNK1 immunoprecipitates (top). Myc-Rac1 proteins were not found in the JNK1 immunoprecipitates. Control immunoblots on total protein extracts (Ext) using anti-Myc or anti-CrkII antibodies are presented.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.