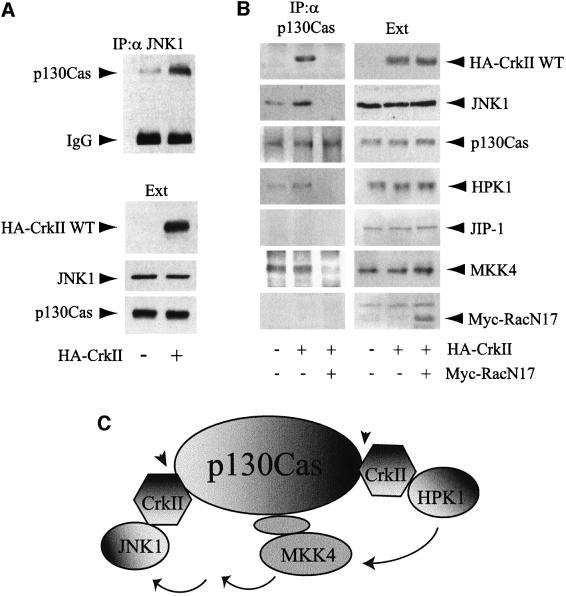
Fig. 5. p130Cas–CrkII as a scaffolding interface for JNK1 that is regulated by Rac1. (A) CrkII overexpression increases the p130Cas–JNK1 interaction. HeLa cells were transfected with HA-CrkII as indicated. The concentrations of transfected HA-CrkII, endogenous p130Cas and JNK1 proteins in the extracts (Ext) were determined after immunoblotting with either anti-HA or polyclonal antibodies for p130Cas and JNK1. Interaction between endogenous forms of p130Cas and JNK1 was determined by immunoprecipitation using anti-JNK1 rabbit polyclonal antibody. The presence of p130Cas in the JNK1 immunoprecipitates was determined using an anti-p130Cas antibody. (B) p130Cas acts as a Rac1-dependent scaffold for JNK1. HeLa cells were either non-transfected or transfected with expression vectors for HA-CrkII or HA-CrkII+Rac1N17. The interaction between p130Cas and several proteins was assayed by immunoprecipitation using a rabbit polyclonal anti-p130Cas antibody followed by western blotting with the corresponding antibodies (left panels). Total amounts of proteins in the extracts (Ext) are shown (right panels). (C) Schematic diagram illustrating the putative role of p130Cas–CrkII as a scaffolding complex for the CrkII→HPK1→MKK4→JNK1 signaling pathway. Several CrkII molecules may interact simultanously with p130Cas since p130Cas is known to contain multiple CrkII binding motifs. Protein–protein interactions that we found to be regulated by Rac1 (see also Figure 2D) are indicated by arrowheads.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.