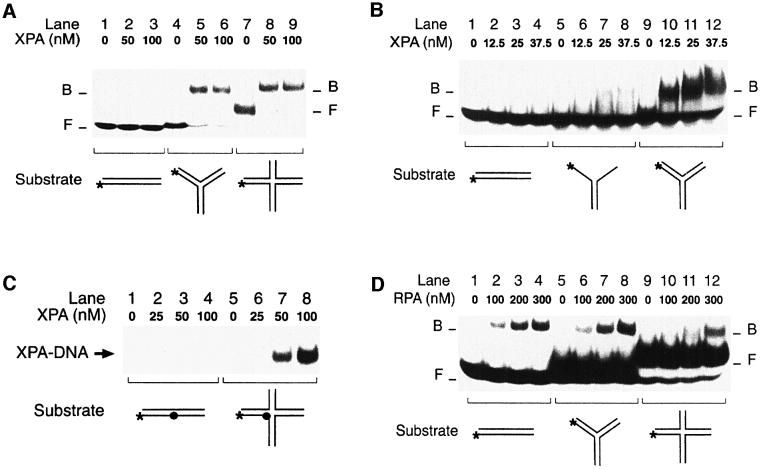
Fig. 5. XPA is an architectural protein that recognizes kinked backbones. (A) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay demonstrating the extraordinary affinity of XPA protein for synthetic three- (lanes 4–6) and four-way DNA junctions (lanes 7–9). (B) Comparison between Y-shaped DNA molecules (lanes 5–8) and three-way DNA junctions (lanes 9–12). (C) XPA can be cross-linked to four-way DNA junctions. Reaction mixtures containing DNA and the indicated concentrations of XPA were pre-incubated for 10 min in the dark, followed by a 20 min exposure to UV light (366 nm). Cross-linked samples were analysed on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel. The filled circle indicates the photoreactive 4-thio-deoxythimidine. (D) Mobility shift assay showing that RPA, unlike XPA, has no increased affinity for three-way junctions (lanes 5–8) or four-way junctions (lanes 9–12) compared with linear duplex DNA (lanes 1–4).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.