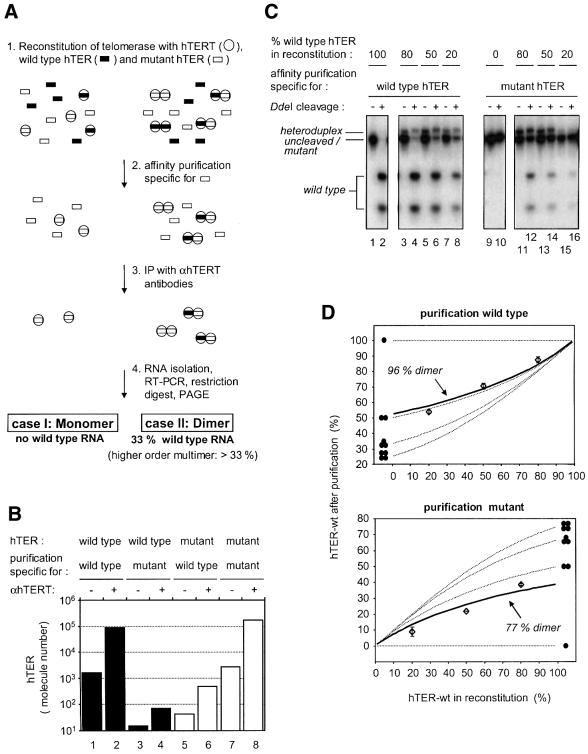
Fig. 4. Telomerase forms a dimer. (A) Scheme for the method used to determine the number of RNA molecules in the telomerase RNP (see text). (B) Affinity purification allows sequence-specific selection of telomerase complexes containing different template sequences. Telomerase was reconstituted with either wild-type or mutant hTER (template sequence: 5′-GAUUGGGAUU-3′), respectively. One half of the mixture was subjected to a purification specific for wild-type hTER and the other half to a purification specific for mutant hTER. The amount of hTER RNA was measured using quantitative RT–PCR following immunoprecipitation with αhTERT antibodies (+) or rabbit IgG (–). (C) Telomerase contains more than one hTER subunit. The experiment depicted schematically in Figure 3A was performed with different mixtures of wild-type and mutant RNA (lanes 3–8, lanes 11–16). RT–PCR products derived from wild-type hTER were cleavable with DdeI (lane 1 and 2) whereas RT–PCR products derived from mutant hTER were lacking this site (lanes 9 and 10). The band that has a slightly lower mobility than the uncleaved/mutant PCR products corresponds to heteroduplex DNA consisting of one wild-type and one mutant strand. (D) Quantitation of the experiment shown in Figure 4C. Data points (open diamonds) with standard deviations and a best-fitted solid line are shown together with theoretical curves (dotted lines) for telomerase being a monomer (labeled with one filled circle), dimer (two filled circles), trimer (three filled circles) or tetramer (four filled circles).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.