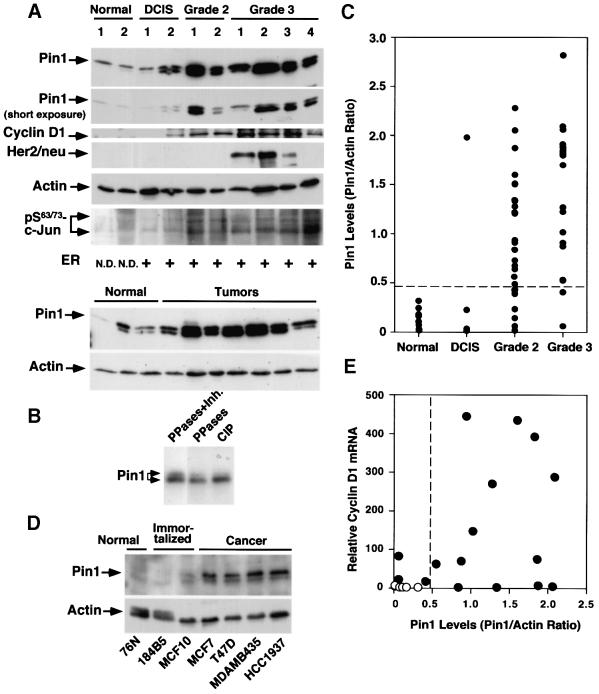
Fig. 2. Pin1 overexpression in human breast cancer cell lines and patient tissues, and its correlation with the Bloom and Richardson grade of tumors. (A) Comparison of Pin1 levels and known breast tumor markers in normal and cancerous human breast tissues. Normal breast and cancer tissues were pulverized in liquid nitrogen, and equal amounts of total protein were separated on SDS-containing gels and transferred to membranes. The membranes were cut into five pieces and subjected to immunoblotting analysis using antibodies to Pin1, cyclin D1, HER2/neu, phosphorylated Ser63/73-c-Jun and actin, respectively. The estrogen receptor status was determined by radioimmunoassay and defined as positive when its levels were >10 fmol/l. The estrogen receptor status in normal controls was not determined (N.D.). Note that Pin1 was detected in immunoblots as a doublet due to phosphorylation. (B) Phosphatase treatment abolishes the double-band pattern of Pin1 in immunoblots. Tumor cell lysates were treated either with a mixture of PP1 and PP2A (PPases) in the presence (lane 1) or absence (lane 2) of the phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid (Inh.), or CIP (lane 3). (C) Pin1 levels in 10 normal breast tissues and different stages of 51 human breast cancer samples. Pin1 levels were determined by immunoblotting analysis, as in (A), and semi-quantified using Imagequant. Actin was used as an internal control, and the Pin1 level in each sample was expressed as the Pin1:actin ratio. (D) Comparison of Pin1 levels in mammary epithelial cell lines. The same amounts of total lysates prepared from normal human mammary epithelial cell lines (Normal), spontaneously immortalized normal human mammary epithelial cell lines (Immortalized) and human breast carcinoma-derived cell lines (Cancer) were subjected to immunoblotting analysis with Pin1 or actin antibodies. (E) Correlation of Pin1 protein levels with cyclin D1 mRNA. RNA was isolated from six normal and 16 cancerous tissues, cDNA synthesized and subjected to real-time PCR for the quantitative analysis of cyclin D1 mRNA expression. The Pearson correlation coefficient was 0.47 (p <0.05).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.