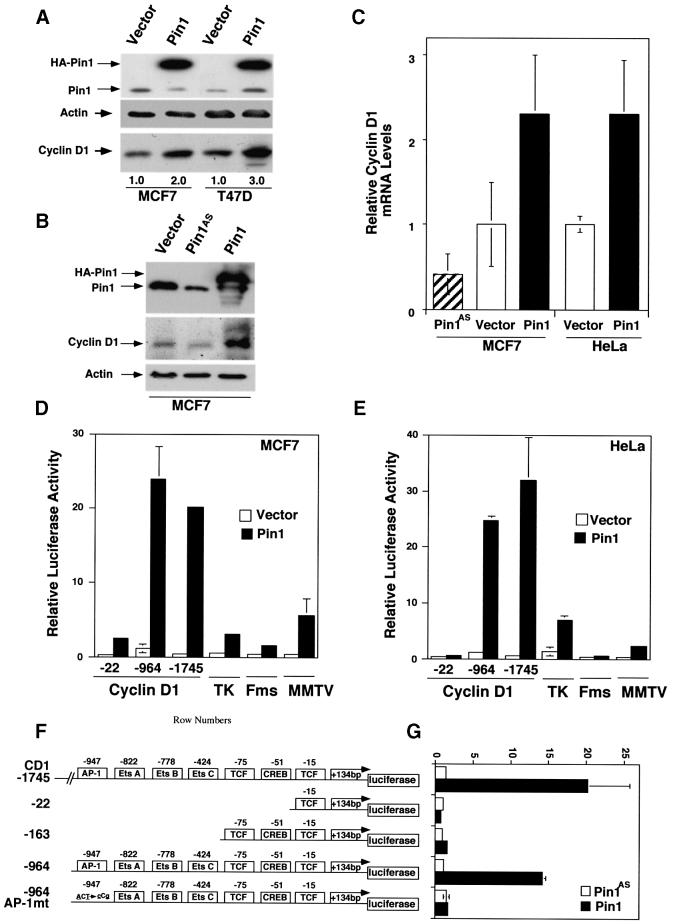
Fig. 3. Pin1 elevates cyclin D1 protein and activates the cyclin D1 promoter via the AP-1 site. (A) Increase in cellular cyclin D1 protein by Pin1. MCF7 or T47D cells were transfected with Pin1 or control vector, followed by immunoblotting analysis of the cell lysates with antibodies against Pin1 and cyclin D1, with actin as a control. Cyclin D1 levels were semi-quantified using Imagequant and are presented below the image; the level in the vector control was defined as 1. (B) Manipulation of Pin1 levels in cells causes changes in cyclin D1 levels. MCF7 cells were transiently transfected with the control vector or a construct expressing HA-Pin1 or antisense Pin1 (Pin1AS), followed by immunoblotting analysis with anti-cyclin D1, -Pin1 or -actin antibodies. (C) Overexpression and depletion of Pin1 increase and decrease levels of cyclin D1 mRNA. MCF7 or HeLa cells were transfected with constructs encoding for Pin1 sense, antisense or vector control as indicated in the figure. After 24 h, mRNA was isolated, cDNA synthesized and subjected to real-time PCR to obtain relative cyclin D1 mRNA levels. (D and E) Activation of cyclin D1, but not TK, c-fms or MMTV promoter by Pin1. MCF7 (D) or HeLa (E) cells were transiently transfected with Pin1 or the vector and various reporter constructs, followed by assaying the luciferase activity. pRL-TK Renilla luciferase reporter construct was co-transfected in each sample to normalize for transfection efficiency. The activity of the reporter luciferase was expressed relative to that in control vector-transfected cells, which is defined as 1. All results are expressed as x̄ ± SD of independent duplicate cultures. Note that to detect the maximal effect of Pin1 on various promoters, we used 0.5 µg of Pin1 cDNA per transfection in this experiment, which was higher than in other experiments described here. (F) Schematic representation of cyclin D1 (CD1) pA3LUC basic reporter constructs and its mutants. Possible transcription factor-binding sites are indicated. –964CD1AP-1mt was same as the wild-type –964CD1construct except for two base-pair substitutions at the consensus AP-1 site. (G) Activation of the cyclin D1 promoter by Pin1 via the AP-1 site. HeLa cells were co-transfected with various cyclin D1 reporter constructs as indicated in (F) and Pin1 sense or antisense (Pin1AS) construct, followed by assaying the luciferase activity. Note that for this experiment 200 ng Pin1 sense or antisense cDNA were used, while in subsequent co-transfection experiments only 50 ng/assay were used.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.