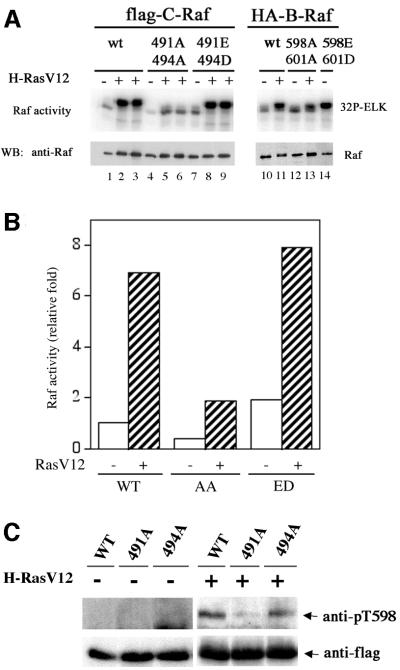
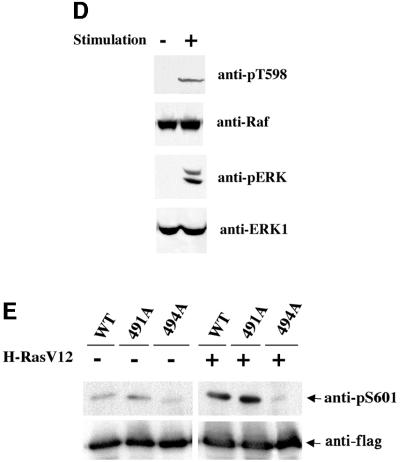
Fig. 2. (A) T491 and S494 are important for C-Raf kinase activation by RasV12. Alanine or acidic residue substitution mutants of C-Raf and B-Raf were transfected with or without RasV12. Raf proteins were immunoprecipitated and assayed for kinase activity as mentioned in Figure 1. C-Raf mutants co-transfected with Ras are shown in duplicate. (B) C-RafT491A/S494A mutant is not stimulated by RasV12. Raf kinase activity was determined by phosphoimage quantitation. The data presented are the average of duplicated assays from a representative experiment. (C) T491 in C-Raf is inducibly phosphorylated. C-Raf wild type, T491A and S494A were transfected with or without RasV12 and resolved for western blotting analysis using anti-pT598 antibody for phosphorylation and anti-Flag for Raf protein level. (D) Stimulation of T491 phosphorylation of endogenous C-Raf by EGF and Raf. HEK293 cells were stimulated with 50 ng/ml EGF and 10% fetal bovine serum for 5 min as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-pT598 antibody or anti-phosphoERK antibody as indicated. The anti-pERK antibody recognizes phosphorylated forms of both ERK1 and ERK2 while the anti-ERK1 antibody recognizes ERK1 protein. (E) Phosphorylation of S494 in C-Raf is stimulated by RasV12. The experiments are similar to (C) except anti-pS601 antibody, which recognizes the phosphorylated S494 in C-Raf, was used.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.