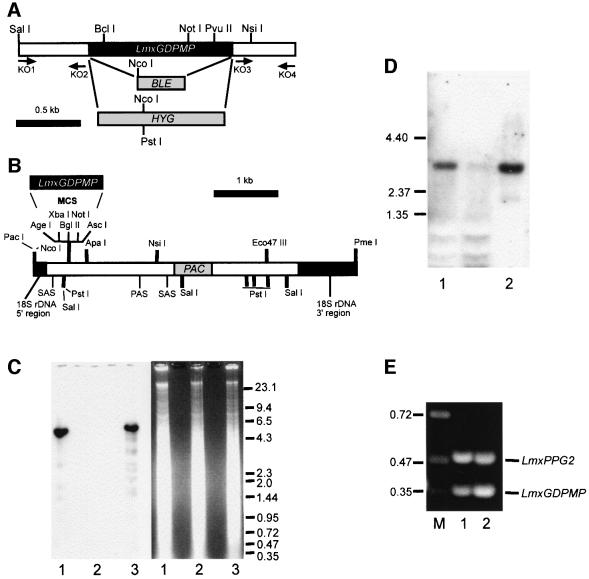
Fig. 2. Targeted gene replacement and gene addback of the LmxGDPMP alleles and analysis of mRNA expression. (A) Restriction maps of the LmxGDPMP locus. The resistance genes BLE and HYG and the primer binding sites (KO1–4) used for the construction of gene deletion cassettes are indicated. (B) Restriction map of the gene addback cassette for genetic rescue of the L.mexicana ΔGDPMP mutant. (C) Southern blot analysis of NcoI–PstI-digested chromosomal DNA (10 µg) from L.mexicana wild type (lane 1), a ΔGDPMP mutant (lane 2) and a ΔGDPMP + cRIBLmxGDPMP gene addback mutant (lane 3). DNA was separated on an ethidium bromide-containing 0.7% agarose gel (right panel), blotted onto a nylon membrane and incubated with a DIG-labeled LmxGDPMP ORF probe (left panel). The sizes of DNA standards are indicated in kilobases. (D) Northern blot analysis of total RNA (10 µg) isolated from L.mexicana log-phase promastigotes (lane 1) and amastigotes (lane 2). RNA was separated on a 0.7% formaldehyde-containing agarose gel, blotted onto a nylon membrane and incubated with a DIG-labeled LmxGDPMP ORF probe. The sizes of RNA standards are indicated in kilobases. (E) Amplification of LmxGDPMP cDNA from L.mexicana log-phase promastigote (lane 1) and amastigote (lane 2) by RT–PCR from total RNA. The loading was normalized to the co-amplified cDNA fragment derived from the LmxPPG2 gene whose mRNA is roughly equally abundant in L.mexicana promastigotes and amastigotes. The sizes of DNA standards are indicated in kilobases.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.