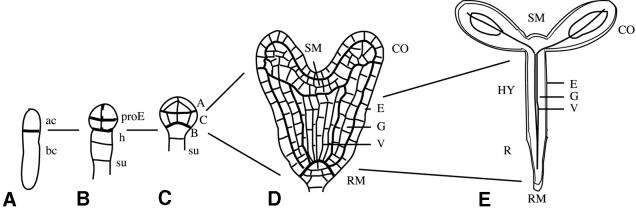
Fig. 1. Development of the apical–basal pattern during Arabidopsis embryogenesis. (A) One-cell stage. The zygote has divided asymmetrically into an apical (ac) and a basal (bc) daughter cell. (B) Octant stage. The proembryo (proE) derived from the apical cell consists of two tiers each of four cells. The basal cell has produced a file of cells, including the hypophysis (h) and the suspensor (su). (C) Dermatogen stage. Three embryo regions are indicated: A, apical; C, central; B, basal. (D) Heart stage. The basic body organization is in place. SM, shoot meristem; CO, cotyledon primordia; RM, root meristem; E, epidermis; G, ground tissue; V, vascular primordium. (E) Seedling. HY, hypocotyl; R, root. Lines indicate the origin of seedling structures from early embryo regions.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.