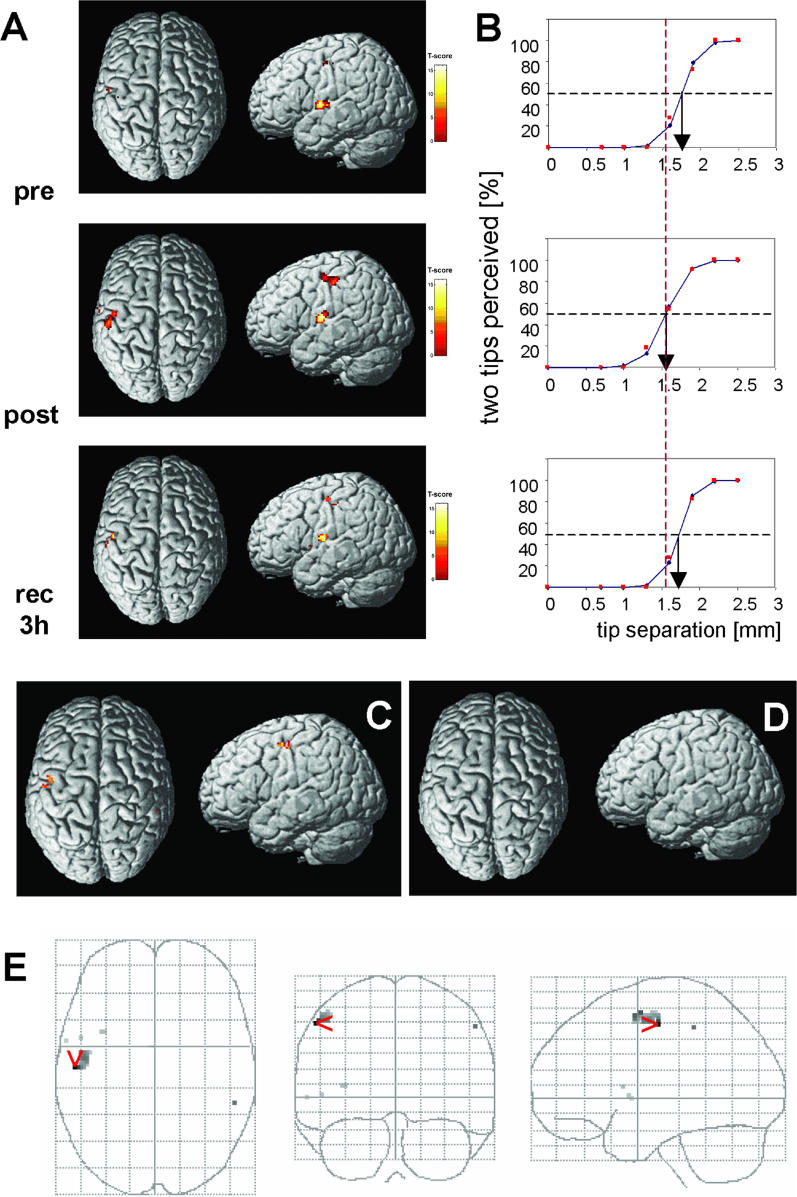
Figure 4. Effects of rTMS on BOLD Signals.
(A) rTMS effect on BOLD signals of a single participant detected pre-rTMS, post-rTMS, and 3 h after rTMS in the left SI ipsilateral to the rTMS site in the postcentral gyrus, and in the contralateral SII in the parietal operculum above the Sylvian fissure. Activations are projected on a rendered T1-weighted MRI dataset. Comparing pre- with post-rTMS fMRI sessions revealed enlarged activation and increased BOLD signal intensity in left SI ipsilateral to the rTMS site. These changes of BOLD signal characteristics recovered 3 h after termination of rTMS.
(B) Psychometric functions illustrating the rTMS-induced improvement of discrimination threshold for the individual shown in (A). Correct responses in percent (red squares) are plotted as a function of separation distance together with the results of a logistic regression line (blue with blue diamonds). 50% levels of correct responses are shown as well as thresholds. Top graph, pre-rTMS; middle graph, post-rTMS condition, immediately after rTMS; bottom graph, recovery after 3 h. After rTMS there is a distinct shift in the psychometric functions towards lower separation distances by 0.20 mm, which recovers to pre-rTMS conditions 3 h later (pre-rTMS, 1.75 mm; recovered, 1.72 mm).
(C) Random-effect analysis (paired t-test pre-post, right D2 stimulation) revealed significant changes of activated patterns localized in SI ipsilateral to the rTMS stimulated D2 representation (n = 12, pre- versus post-rTMS; threshold, p = 0.001, uncorrected for multiple comparisons; S1-parameters, 32 voxels; T-score = 4.15; x,y,z (mm), −54, −14, 50; Talairach position, postcentral gyrus, Brodmann area 3).
(D) No changes of BOLD activity were found in the right hemisphere contralateral to the rTMS site (paired t-test pre- versus post-rTMS, left index finger stimulation; threshold, p = 0.001, uncorrected for multiple comparisons) and in SII.
(E) Changes in activation pattern as obtained from random effects analysis (paired t-test pre- versus post-rTMS, right index finger stimulation; compare with [C]), superimposed on a glass brain for visualization. Views are from top (left grid), back (middle grid), and right (right grid).