Figure 2.—
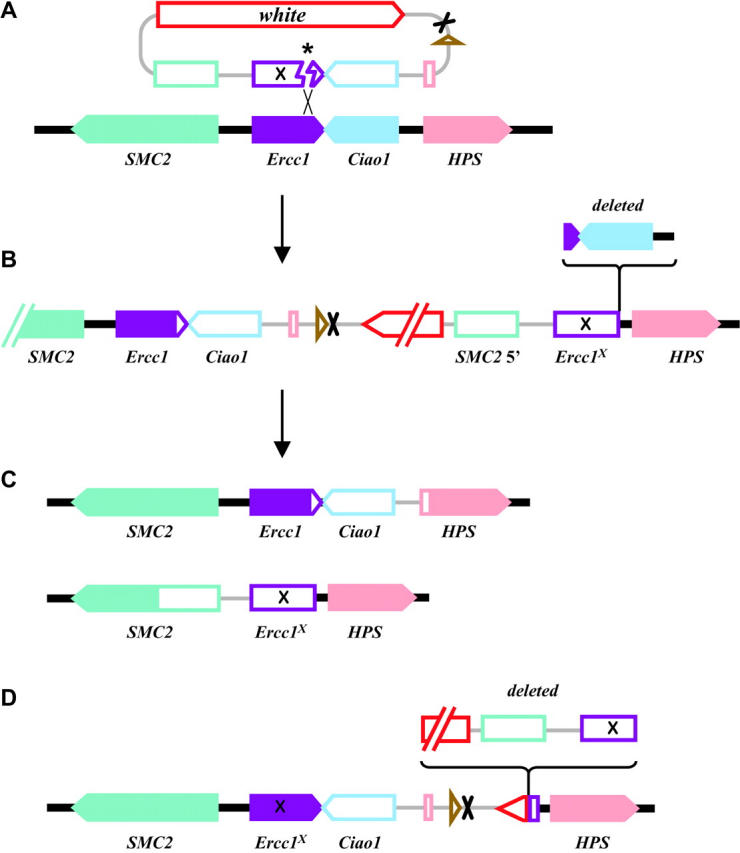
Targeting of Ercc1. (A) Genes from the Ercc1 genomic region are shown as solid arrows (indicating direction of transcription) on a solid line, and genes on the targeting DNA are shown as open arrows or boxes on a shaded line. The targeting DNA is shown after excision by FLP recombinase and cutting by I-SceI endonuclease, with an asterisk marking the site of the double-strand break. This targeting fragment is drawn to show alignment of sequences with homology between the targeting DNA and the genomic DNA. The XhoI site introduced into Ercc1 is indicated by an X. The mini-white marker gene and the FRT and I-CreI sites are as in Figure 1. (B) The predicted product of ends-in integration with sequences derived from the targeting DNA in open symbols and chromosomal sequences as solid symbols. The region deleted in the integration that we recovered is indicated. (C) Predicted products from reduction of the tandem duplication after cutting with I-CreI and repair by single-strand annealing. One product is completely wild type (top), and the other carries Ercc1X and the adjacent deletion of Ciao1 (bottom). (D) The structure of the mutation used in these studies. It is equivalent to the targeted integration depicted in B, except that most of mini-white and one copy of Ercc1 have been deleted, and the remaining copy of Ercc1 carries the XhoI mutation.
