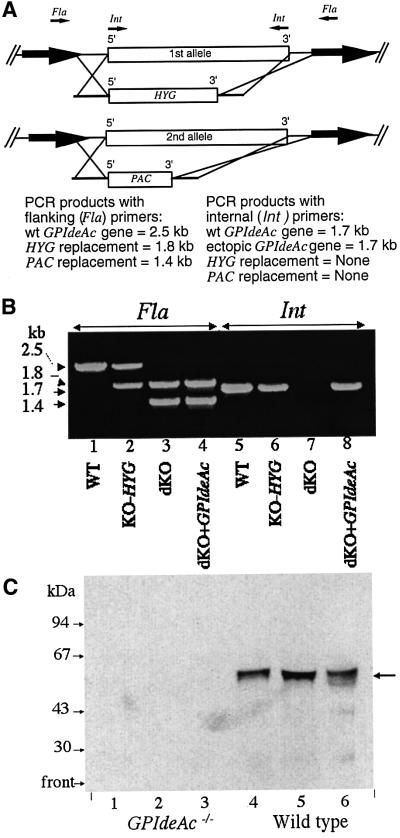
Fig. 6. Construction and characterization of GPIdeAc–/– double knockout and conditional mutants. (A) The first GPIdeAc allele was replaced by HYG and the second by PAC. The targeting sequences used for homologous recombination were designed to avoid two adjacent potential ORFs (bold arrows). PCR primers were designed to DNA regions flanking (Fla) the recombination regions and internal (Int) to the GPIdeAc ORF. (B) PCR products from DNA extracted from wild-type cells (WT; lanes 1 and 5), single knockout cells (KO-HYG; lanes 2 and 6), double knockout cells (dKO; lanes 3 and 7) and double knockout cells with a tetracycline-inducible HA-tagged ectopic copy of GPIdeAc (dKO + GPIdeAc; lanes 4 and 8) using flanking (Fla; lanes 1–4) and internal (Int; lanes 4–8) primers, as indicated. (C) Membranes from wild-type and GPIdeAc–/– double knockout mutants were labelled with [3H]DFP and processed as described in Figure 2A. The ConA–agarose beads were eluted twice with α-methyl-mannoside (lanes 1 and 2, and 4 and 5) and finally boiled in SDS sample buffer (lanes 3 and 6). The samples were subjected to SDS–PAGE and fluorography.
