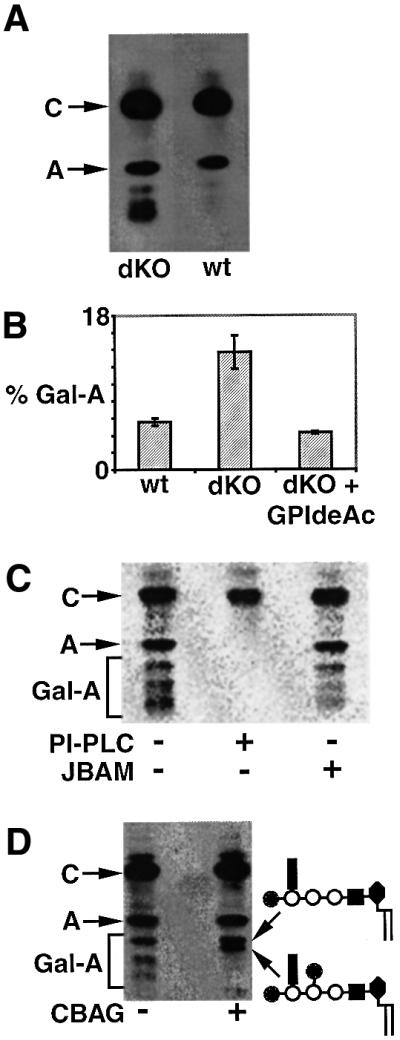
Fig. 9. GPIdeAc–/– cells accumulate polar galactosylated GPI species. (A) Wild-type (wt) and GPIdeAc–/– double knockout (dKO) cells were metabolically labelled with [3H]mannose and the radiolabelled glycolipids were analysed by HPTLC and fluorography. The dKO cells produced glycolipid A and substantial amounts of more polar glycolipids running between glycolipid A and the origin. (B) wt, dKO and dKO cells expressing GPIdeAc–HA (dKO + GPIdeAc–HA) were labelled and the glycolipids analysed as described above, except that a phosphorimager was used to quantify the proportion of polar glycolipids running between glycolipid A and the origin (mean ± SEM for triplicate measurements are shown). (C) Glycolipids labelled in dKO cells were analysed by HPTLC and phosphorimager with (+) and without (–) PI-PLC and jack bean α-mannosidase (JBAM) digestion. (D) Glycolipids labelled in dKO cells were analysed by HPTLC and fluorography with (+) and without (–) coffee bean α-galactosidase (CBAG) digestion. The terminal digest produced glycolipid A and, most likely, the two α-galactosidase-resistant galactosylated glycolipid A products (Mehlert et al., 1998) shown on the right.
