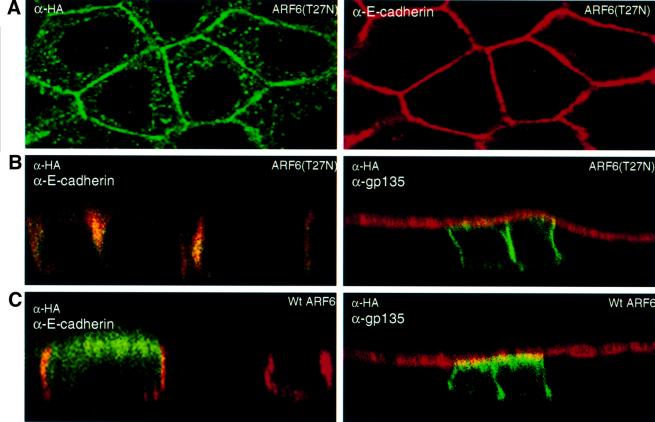
Fig. 6. Subcellular distribution of ARF6(T27N) and wild-type ARF6. (A) Cells expressing HA-tagged ARF6(T27N) were double labeled with anti-HA rabbit polyclonal antibody (green) and anti-E-cadherin mouse monoclonal antibody (red). An image across a single confocal plane at the cell junctions is shown to emphasize the localization of ARF6(T27N) at the cell junctions. (B) Cells expressing HA-tagged ARF6(T27N) were double labeled for HA (green) and for either E-cadherin (red, shown on the left) or gp135 (red, shown on the right). Coincident red and green staining appears yellow. Merged images taken along the x/z-axis are shown. ARF6(T27N) localizes to the AJs of MDCK cells; a small fraction of label was also seen at the lateral membrane and subapical region. (C) Cells transiently expressing HA-tagged wild-type (wt) ARF6 were labeled for HA (green) and for either E-cadherin (red, left) or gp135 (red, right). Coincident red and green staining appears yellow. Merged images taken along the x/z-axis are shown. Wild-type ARF6 localizes to the AJs, the lateral membrane and subapical membranes.
