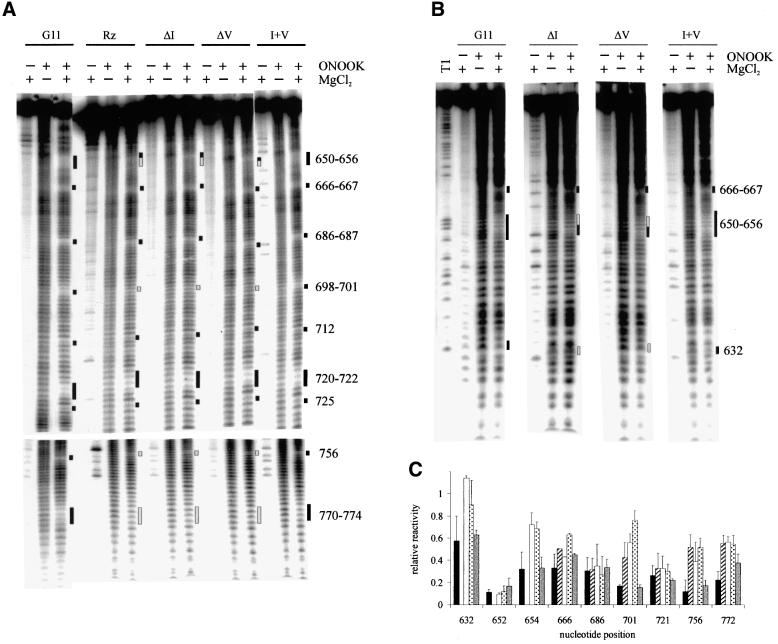
Fig. 4. Hydroxyl radical protection patterns in mutant VS RNAs. Reactions were carried out in the presence or absence of ONOOK and/or 20 mM MgCl2 for the trans-cleaving ribozyme (Rz) and the downstream cleavage products of each of the other RNAs indicated at the top of the figure. Positions protected from cleavage as in wild-type G11 D RNA are indicated by black bars. Positions where the protections are compromised or absent in the mutants with a disrupted kissing-interaction are indicated by gray bars. RNAs were labeled at their 3′ (A) or 5′ (B) end and electrophoresed for times appropriate to resolve regions of protection. (C) Relative reactivity (y-axis) of representative protected positions (x-axis) in the presence of 20 mM MgCl2. The solid, striped, open, dotted and gray bars represent the reactivities of G11, Rz, ΔI, ΔV and I + V RNAs, respectively. The data are the mean of two to five repeats; error bars represent the standard deviations.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.