Full text
PDF
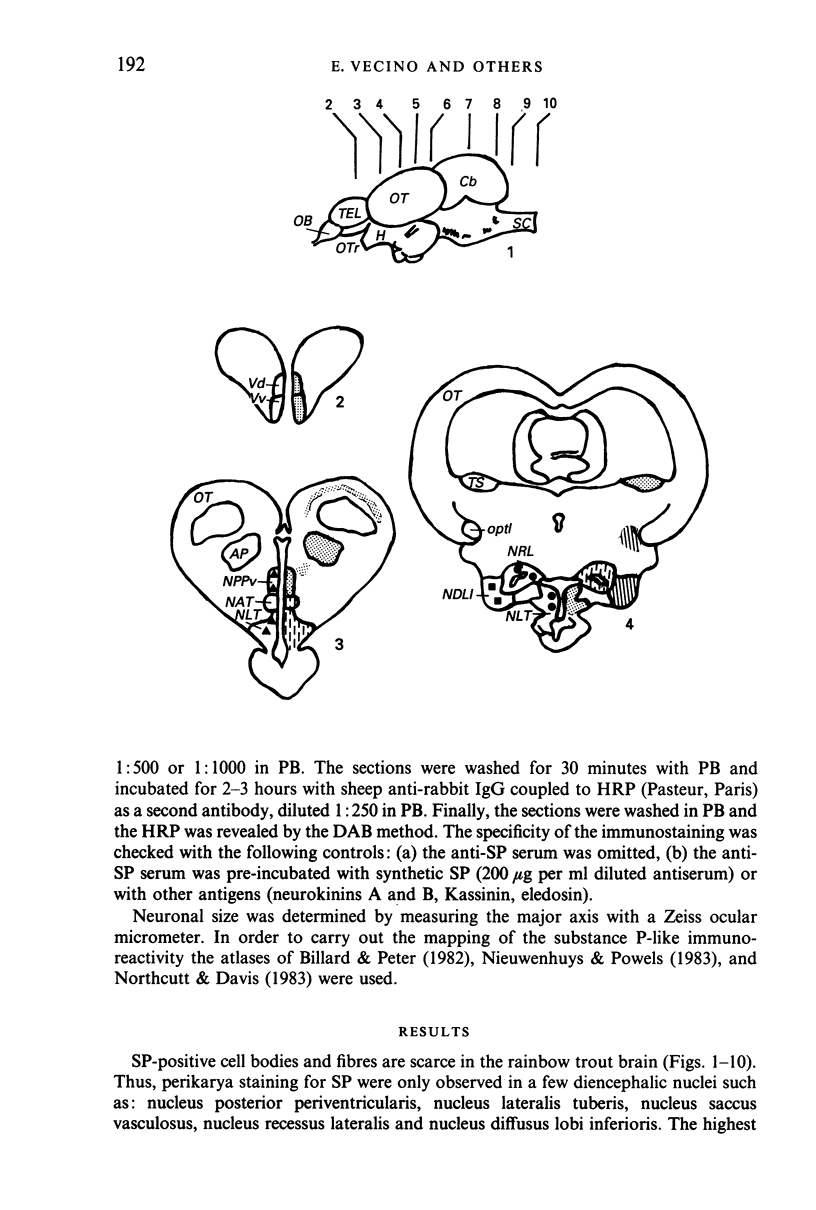
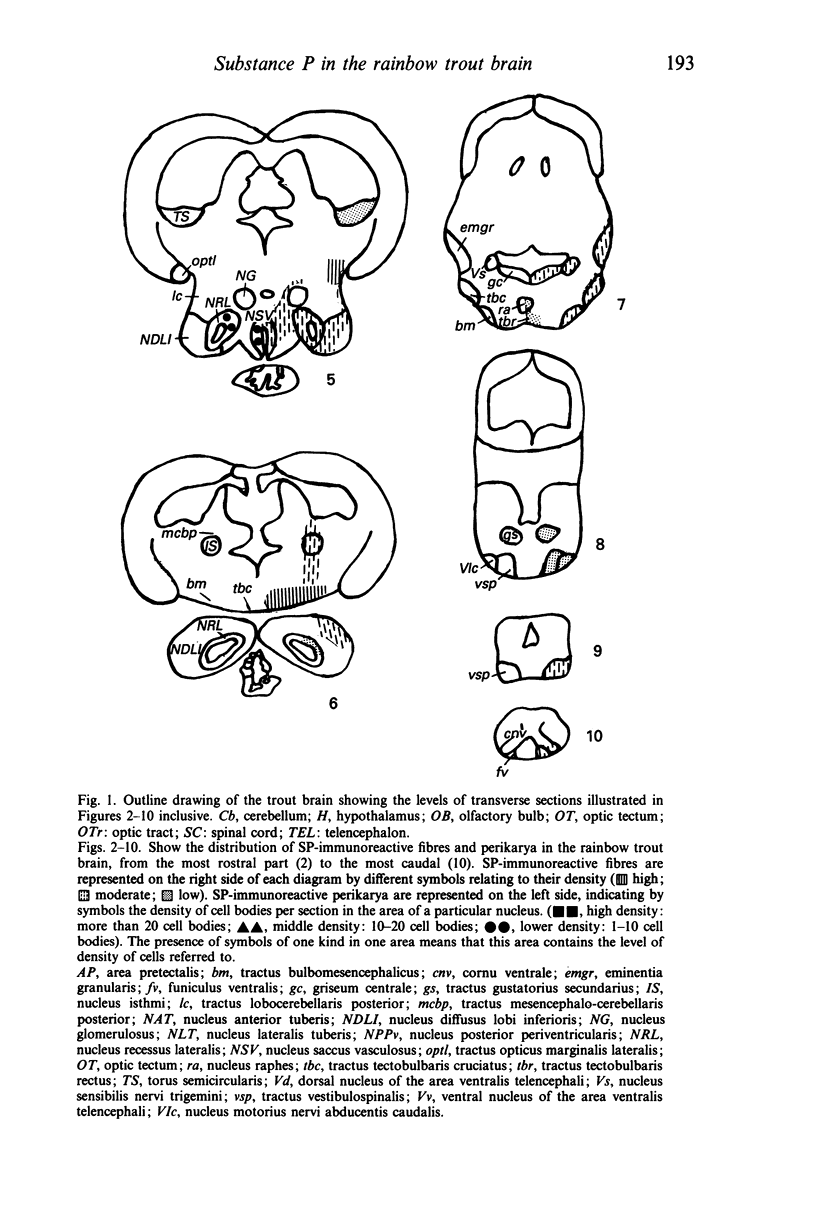







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayorh M. A., Feuerstein G. Bombesin and substance P modulate peripheral sympathetic and cardiovascular activity. Peptides. 1985;6 (Suppl 1):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billard R., Peter R. E. A stereotaxic atlas and technique for nuclei of the diencephalon of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Reprod Nutr Dev. 1982;22(1A):1–25. doi: 10.1051/rnd:19820101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjenning C., Holmgren S. Neuropeptides in the fish gut. An immunohistochemical study of evolutionary patterns. Histochemistry. 1988;88(2):155–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00493298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouras C., Vallet P. G., Dobrinov H., de St-Hilaire S., Constantinidis J. Substance P neuronal cell bodies in the human brain: complete mapping by immunohistofluorescence. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Aug 15;69(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90409-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet J. F., Delaleu J. C., Holley A. Réponses électriques de la muqueuse olfactive de Grenouille à l'application d'acétylcholine et de substance P. C R Acad Sci III. 1984;298(6):169–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brauth S. E., Reiner A., Kitt C. A., Karten H. J. The substance P-containing striatotegmental path in reptiles: an immunohistochemical study. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Sep 20;219(3):305–327. doi: 10.1002/cne.902190306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., KAPLAN M. H. Localization of antigen in tissue cells; improvements in a method for the detection of antigen by means of fluorescent antibody. J Exp Med. 1950 Jan 1;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuello A. C., Kanazawa I. The distribution of substance P immunoreactive fibers in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Mar 1;178(1):129–156. doi: 10.1002/cne.901780108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du F., Charnay Y., Dubois P. Development and distribution of substance P in the spinal cord and ganglia of embryonic and newly hatched chick: an immunofluorescence study. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Sep 15;263(3):436–454. doi: 10.1002/cne.902630309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekström P., Korf H. W. Substance P-like-immunoreactive neurons in the photosensory pineal organ of the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson (Teleostei). Cell Tissue Res. 1986;246(2):359–364. doi: 10.1007/BF00215898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekström P., Van Veen T. Distribution of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) in the brain of the teleost Gasterosteus aculeatus L. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Jul 1;226(3):307–320. doi: 10.1002/cne.902260302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. J. Neurophysiological effects of opiates in the CNS. Monogr Neural Sci. 1987;13:132–160. doi: 10.1159/000414574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren S., Grove D. J., Nilsson S. Substance P acts by releasing 5-hydroxytryptamine from enteric neurons in the stomach of the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Neuroscience. 1985 Feb;14(2):683–693. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90319-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren S., Vaillant C., Dimaline R. VIP-, substance P-, gastrin/CCK-, bombesin-, somatostatin- and glucagon-like immunoreactivities in the gut of the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;223(1):141–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00221505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki S., Senba E., Shiosaka S., Takagi H., Kawai Y., Takatsuki K., Sakanaka M., Matsuzaki T., Tohyama M. Regional distribution of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the frog brain and spinal cord: immunohistochemical analysis. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Sep 10;201(2):243–254. doi: 10.1002/cne.902010208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kah O., Chambolle P. Serotonin in the brain of the goldfish, Carassius auratus. An immunocytochemical study. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;234(2):319–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00213771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuljis R. O., Karten H. J. Laminar organization of peptide-like immunoreactivity in the anuran optic tectum. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Dec 1;212(2):188–201. doi: 10.1002/cne.902120208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. B., Marshak D. W., Dowling J. E., Lam D. M. Colocalization of immunoreactive substance P and neurotensin in amacrine cells of the goldfish retina. Brain Res. 1986 Feb 26;366(1-2):307–313. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl A., Hökfelt T., Nilsson G. Distribution of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat--I. Cell bodies and nerve terminals. Neuroscience. 1978;3(10):861–943. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mai J. K., Stephens P. H., Hopf A., Cuello A. C. Substance P in the human brain. Neuroscience. 1986 Mar;17(3):709–739. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshak D. W., Carraway R. E., Ferris C. F. Characterization of immunoreactive substance P and neurotensin in the goldfish retina. Exp Eye Res. 1987 Jun;44(6):839–848. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(87)80046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olpe H. R., Heid J., Bittiger H., Steinmann M. W. Substance P depresses neuronal activity in the rat olfactory bulb in vitro and in vivo: possible mediation via gamma-aminobutyric acid release. Brain Res. 1987 Jun 2;412(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91133-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent A., Dube L., Braford M. R., Jr, Northcutt R. G. The organization of monoamine-containing neurons in the brain of the sunfish (Lepomis gibbosus) as revealed by fluorescence microscopy. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Dec 1;182(3):495–516. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner A., Northcutt R. G. An immunohistochemical study of the telencephalon of the African lungfish, Protopterus annectens. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Feb 15;256(3):463–481. doi: 10.1002/cne.902560313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reubi J. C., Jessell T. M. Distribution of substance P in the pigeon brain. J Neurochem. 1978 Jul;31(1):359–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12471.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie T. C., Leonard R. B. Immunohistochemical studies on the distribution and origin of candidate peptidergic primary afferent neurotransmitters in the spinal cord of an elasmobranch fish, the Atlantic stingray (Dasyatis sabina). J Comp Neurol. 1983 Feb 1;213(4):414–425. doi: 10.1002/cne.902130406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo T., Blähser S., Denizot J. P., Véron-Ravaille M. High substance P-like immunoreactivity (SPLI) in the olfactory and electrosensory cells of gymnotid fish. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Oct 29;81(3):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terlou M., Ekengren B., Hiemstra K. Localization of monoamines in the forebrain of two salmonid species, with special reference to the hypothalamo-hypophysial system. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Jul 10;190(3):417–434. doi: 10.1007/BF00219556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terlou M., Ekengren B. Nucleus praeopticus and nucleus lateralis tuberis of Salmo salar and Salmo gairdneri: structure and relationship to the hypophysis. Cell Tissue Res. 1979 Mar 9;197(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00233550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Rascher W., Schuster C., Pavlovitch R., Schömig A., Dietz R., Ganten D. Central blood pressure effects of substance P and angiotensin II: role of the sympathetic nervous system and vasopressin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 24;71(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90384-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- V Euler U. S., Gaddum J. H. An unidentified depressor substance in certain tissue extracts. J Physiol. 1931 Jun 6;72(1):74–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1931.sp002763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanegas H., Laufer M., Amat J. The optic tectum of a perciform teleost. I. General configuration and cytoarchitecture. J Comp Neurol. 1974 Mar 1;154(1):43–60. doi: 10.1002/cne.901540104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessendorf M. W., Elde R. The coexistence of serotonin- and substance P-like immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of the rat as shown by immunofluorescent double labeling. J Neurosci. 1987 Aug;7(8):2352–2363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]