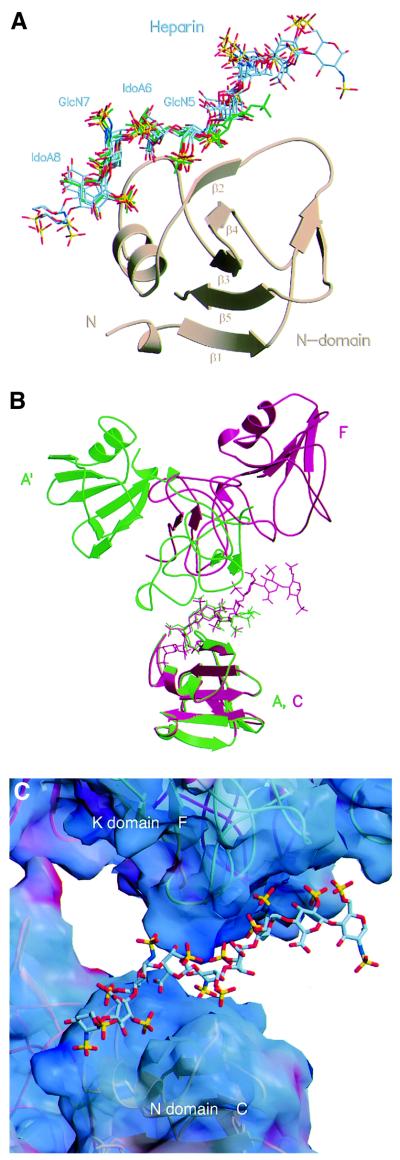
Fig. 2. The heparin-binding site of NK1 and the interaction between heparin and the K domain. (A) Superposition of the N domain of protomer A from crystal type A and protomers B, C, F, G and H from crystal type B. The resulting position of the heparin molecules bound to these N domains shows a highly conserved binding motif for GlcN-5, IdoA-6, GlcN-7 and IdoA-8. The heparin molecule of the high-resolution structure of crystal type A is coloured in green. (B) Superposition of the N domain of protomer A in crystal type A (green), and protomer C in crystal type B (red). The resulting position of the corresponding K domains (the K domain of a symmetry-related protomer A′ in crystal type A and the K domain of protomer F in crystal type B) shows different positions relative to heparin, although the same patch of residues is involved in the contacts. (C) Surface electrostatic potential of NK1 at the site of interaction with heparin molecule X. Surface areas corresponding to positive potential are shown in blue, areas with negative potential are shown in red. The heparin is positioned in a positively charged groove between the N domain of protomer C and the K domain of protomer F. Electrostatic potential was calculated with GRASP (Nicholls et al., 1991).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.