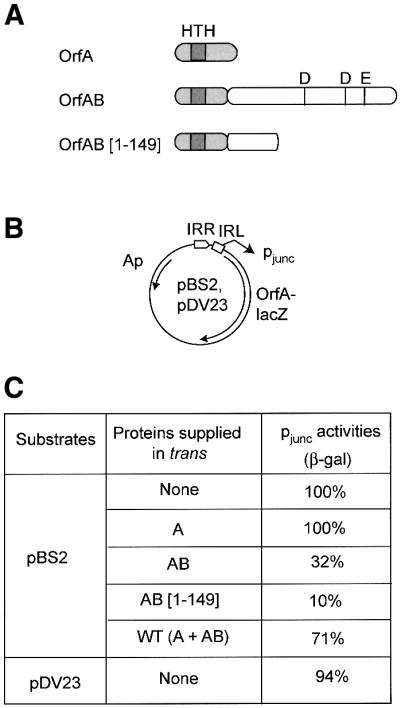
Fig. 7. Effect of IS911-encoded proteins on pjunc activity measured by β-galactosidase assays. (A) The proteins. Four protein configurations were tested: OrfA, OrfAB, a truncated derivative of OrfAB, OrfAB[1–149], deleted for the C-terminal catalytic domain and OrfA + OrfAB (wild-type configuration). The proteins are shown schematically illustrating the relative position of the catalytic DDE motif and of a helix–turn–helix motif potentially involved in DNA binding. The proteins were supplied in trans under control of placUV5. from plasmids pAPT156 (OrfA), pAPT111 (OrfAB), pLH114 (OrfAB[1–149]), and pAPT112 (OrfA + OrfAB). pAPT110 was used as a control without IS911 proteins. (B) The test plasmids. pBS2 carries mutations in the terminal dinucleotides at both ends in the IRR–IRL junction. pDV23 carries a wild-type IRR–IRL junction. Symbols are as described in Figures 3, 4 and 5. (C) β-galactosidase activities. The right hand column indicates β-galactosidase activities as a percentage relative to pjunc activity in the absence of any proteins in trans (100%). These results are the average of three independant experiments with a standard error of ∼15%. pDV23 (active junction) was tested in the absence of proteins supplied in trans to ensure that the terminal dinucleotide mutations (5′-CA to 5′-AG) introduced to inactivate integration activity of the junction did not affect pjunc activity.100% = 17 500 Miller units.
