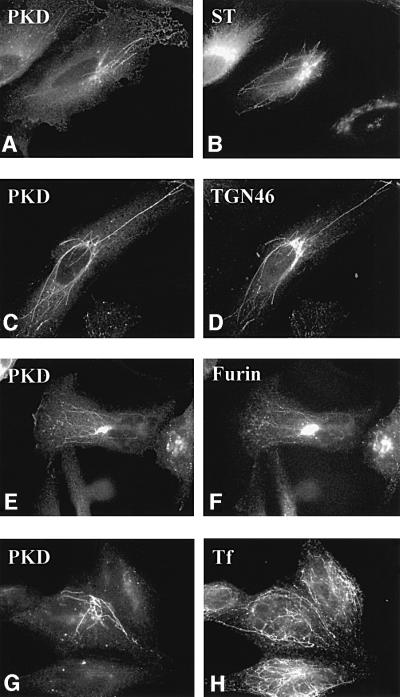
Fig. 1. Wild-type PKD localizes to TGN. HeLa cells were transfected with GST–PKD (C, D, G and H) alone or co-transfected with GFP–sialyltransferase (A and B) or EGFP–furin (E and F). The cells were treated with BFA for 6 min (A and B) or 10 min (C–H), fixed and stained with anti-phospho-PKD (A, C, E and G), anti-TGN46 (D) and anti-transferrin (H) antibodies. For early endosome staining, as described in Materials and methods, the cells were incubated with pre-incubation medium for 1 h, followed by incubation with iron-saturated transferrin for 15 min prior to BFA treatment (G and H). BFA induced tubulation of the early Golgi cisternae, TGN and the endosomes. PKD co-localizes with TGN46 (C and D) and furin (E and F), but not sialyltransferase (A and B) and transferrin (G and H). Thus, PKD is contained in the portion of the TGN containing furin and TGN46. Interestingly, under these conditions, the peripheral Golgi proteins COPI coats are detached; PKD, however, remains attached to theTGN-derived tubes.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.