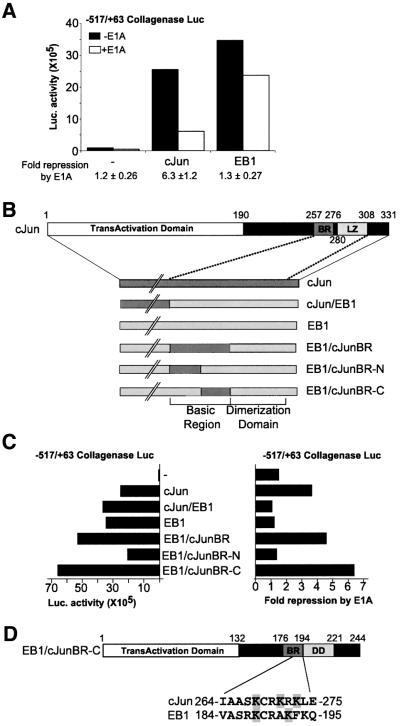
Fig. 1. Transcription factor-specific repression of the collagenase promoter by E1A requires a 12 amino acid region in the c-Jun basic region. (A) E1A specifically represses the c-Jun- and not the EB1-activated collagenase promoter (+517/–63). F9 cells were transfected with collagenase promoter–luciferase reporter and c-Jun or EB1 in the absence (black bars) or presence (white bars) of E1A. The average fold repression ± SD by E1A of six experiments is shown below the graph. (B) Schematic representation of c-Jun–EB1 chimeras. Full-length c-Jun with its functional domains: the N-terminal transactivation domain (TAD) and the C-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD) consisting of the basic region (BR) and the leucine zipper (LZ). The chimeras of c-Jun (dark grey) and EB1 (light grey) are depicted, showing the basic region (BR) and dimerization domain (DD) enlarged. (C) Luciferase activity after co-transfection of the collagenase promoter–luciferase reporter with the c-Jun/EB1 chimeras in F9 cells. On the left the activity of the chimeras on the collagenase promoter is shown. On the right the fold repression by E1A of the collagenase promoter–luciferase reporter activated with the chimeras is shown. (D) Schematic representation of EB1/c-JunBR-C, which consists of EB1 with the 12 amino acid sequence of c-Jun substituting for the indicated homologous EB1 sequence.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.