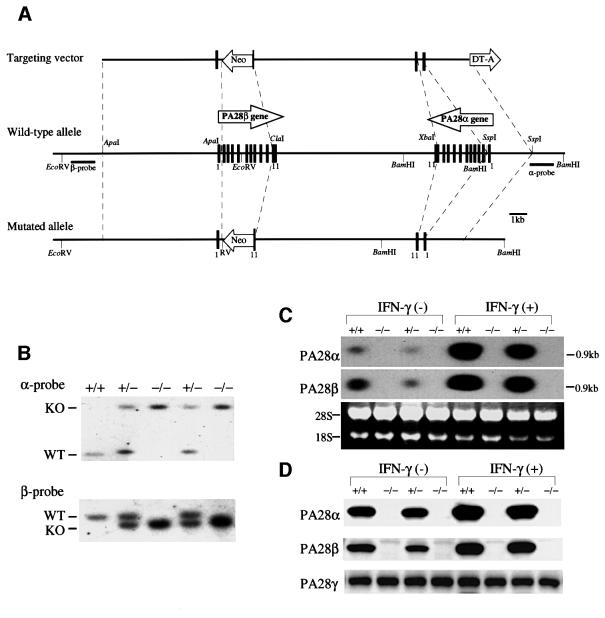
Fig. 1. Disruption of the PA28α and PA28β genes by homologous recombination. (A) Structure of the targeting vector, the wild-type PA28α/β genes and the mutated PA28α/β genes following homologous recombination. Relevant restriction enzyme sites are indicated. Exons are depicted as closed boxes. The first and the last exons of the PA28α/β genes are numbered 1 and 11, respectively. The probes used for Southern blot analysis are shown as α- and β-probes. (B) Southern blot analysis. Genomic DNA extracted from mouse tails was digested with BamHI or EcoRV, blotted, and hybridized with the α- or the β-probe shown in (A), respectively. The wild-type allele (WT) gave a 2.5 kb fragment for the α-probe and a 9.0 kb fragment for the β-probe, while the mutant allele (KO) gave a 4.8 kb fragment for the α-probe and a 7.5 kb fragment for the β-probe. (C) Northern blot analysis. Total RNAs isolated from MEFs cultured with or without IFN-γ for 36 h were hybridized with the full-length mouse PA28α or PA28β cDNA probe. 28S and 18S rRNAs were stained with ethidium bromide to monitor the integrity of RNA. (D) Western blot analysis. Protein lysates from MEFs cultured with or without IFN-γ for 72 h were used to examine the expression of PA28α, β and γ.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.