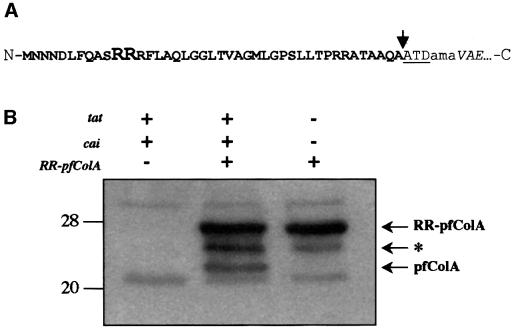
Fig. 2. (A) Schematic representation of the amino acid sequence at the junction point of the hybrid RR–pfColA. The twin-arginine signal peptide is represented in bold letters, with the RR residues of the twin-arginine motif in a larger font size. The pfColA amino acid sequence is in italics. The added linker region in the hybrid proteins is indicated in lower case letters. The leader peptidase cleavage site is indicated by an arrow and is followed by the first three residues of the mature TorA protein (ATD). N and C indicate the N- and C-termini of the protein, respectively. (B) Tat-dependent processing of RR–pfColA. The presence (+) or absence (–) of the tat, cai and RR–pfcolA genes for each cell sample is indicated. Whole-cell extracts of E.coli wild-type strains containing pImTc and pRR-pfColA or the vector pMMB67EH, and the E.coli tat mutant (tatABCDE) containing pRR-pfColA were loaded on an 11% acrylamide gel containing SDS, and proteins were separated by electrophoresis and blotted onto nitrocellulose. The immunoblot was revealed using antibodies directed against pfColA (diluted 1:1000). The arrow indicates the position of the precursor (RR–pfColA) and mature (pfColA) proteins. The deduced mol. wts of 26.6 and 22.8 kDa are in agreement with the expected size of RR–pfColA and pfColA, respectively. The asterisk indicates the position of a putative degradation product. Molecular weight markers are indicated on the left.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.